2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione isolated from Averrhoa carambola L. root ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 31496773
- PMCID: PMC6689538
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S209436
2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione isolated from Averrhoa carambola L. root ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway
Erratum in
-
Erratum: 2-Dodecyl-6-Methoxycyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione Isolated from Averrhoa carambola L. Root Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy by Inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway [Corrigendum].Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Dec 16;13:5015. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S295043. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 33376370 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Averrhoa carambola L. is a traditional medicinal herb that has long been used to treat diabetes. Our previous studies found that 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione (DMDD) isolated from A. carambola L. roots could ameliorate diabetic nephropathy (DN), but its exact mechanism remains unclear.
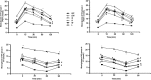
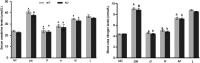
Methods: A DN model was established by streptozotocin (STZ, 100 mg/kg body weight) in TLR4 knockout (TLR4-/-, KO) mice and wild-type (WT) mice. Body weight and blood glucose were evaluated after oral administration of DMDD (12.5, 25, 50 mg/kg body weight/d) in diabetic mice. The levels of serum lipids, including TC, TG, HDL, and LDL and kidney function indexes Scr and BUN, were detected by biochemical equipment. The levels of inflammatory cytokines including IL-6 and TNF-α, were determined by ELISA kits. Furthermore, changes in renal ultrastructure were observed by electron microscopy. Western blot analysis and RT-PCR were used to assess the protein expression and mRNA levels of TLR4, MyD88 and NF-κB.
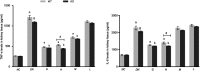
Results: DMDD treatment attenuated diabetic nephropathy, as a result of a decline in blood glucose, serum creatinine, and blood urine nitrogen levels and an increase in the quantity and density of podocytes, combined with improved dyslipidaemia. DMDD treatment inhibited the inflammatory response and downregulated the expression of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in diabetic mice, and these changes were significantly different in TLR4-/- mice.
Conclusion: DMDD alleviates diabetic nephropathy by mitigating kidney damage and inflammation via the inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway.
Keywords: 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione; TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway; diabetic nephropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
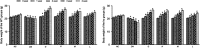
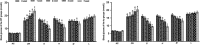


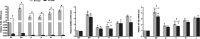


References
-
- Allison SJ. Acute kidney injury:Mechanism of AKI sensitivity in diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10(9):484. - PubMed
-
- Zheng N, Lin X, Wen Q, et al. Effect of 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione, isolated from Averrhoa carambola L. (Oxalidaceae) roots, on advanced glycation end-product-mediated renal injury in type 2 diabetic KKAy mice. Toxicol Lett. 2013;219(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.03.001 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

