Association between polymorphisms of LEP, LEPR, DRD2, HTR2A and HTR2C genes and risperidone- or clozapine-induced hyperglycemia
- PMID: 31496784
- PMCID: PMC6689662
- DOI: 10.2147/PGPM.S210770
Association between polymorphisms of LEP, LEPR, DRD2, HTR2A and HTR2C genes and risperidone- or clozapine-induced hyperglycemia
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether genetic polymorphisms related to pharmacodynamics with metabolic adverse effects, namely leptin promoter (LEP) rs7799039, leptin receptor rs1137101, dopamine D2 rs4436578, serotonin 5-HT2A rs6313, and serotonin 5-HT2C rs518147 and rs12836771, are associated with hyperglycemia induced by risperidone or clozapine in adult Thai patients with psychosis.
Methods: A total of 180 patients treated with risperidone-based (n=130) or clozapine-based (n=50) regimens were included in this study. Blood samples were analyzed for genotyping of the candidate genes and biochemical testing. Genotyping was performed by conducting a TaqMan real-time polymerase chain reaction-based analysis.
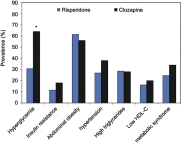
Results: The prevalence of hyperglycemia was higher in patients receiving clozapine (64.0%) than in those receiving risperidone (30.8%). Among the candidate genes, only the LEP rs7799039 polymorphism demonstrated a significant association with hyperglycemia (χ2=9.879, P=0.008) in patients treated with risperidone; patients with the AA genotype had the highest risk (41.1%), followed by those with AG (20.8%) and GG (0%) genotypes. Using the recessive genetic model (AA vs AG + GG), the odds ratio and 95% CI were 3.28 and 1.44 -7.50, respectively. None of the genes were associated with hyperglycemia in patients treated with clozapine. A binary logistic regression revealed that the LEP rs7799039 polymorphism demonstrated a significant association with hyperglycemia, independent of body-mass index (BMI) in patients receiving risperidone; the odds ratio (95% CI) was 3.188 (1.399-7.262), P=0.006. By contrast, none of the pharmacodynamic genetic factors, except for BMI, were significantly associated with hyperglycemia in patients receiving clozapine.
Conclusion: The risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with the LEP rs7799039 polymorphism in Thai adults receiving risperidone but not in those receiving clozapine. Clarifying underlying mechanisms and risk of hyperglycemia provides an opportunity to prevent impaired glucose metabolism in patients receiving risperidone or clozapine.
Keywords: atypical antipsychotics; diabetes mellitus; dopamine D2; leptin promoter; leptin receptor; serotonin 5-HT2A; serotonin 5-HT2C.
Conflict of interest statement
The abstract of this paper was presented at the 70th AACC Annual Scientific Meeting as a poster presentation with interim findings. The poster’s abstract was published in “Abstract Guide” in poster sessions: Endocrinology/Hormones. All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous