The expression of microRNA 146a in patients with ischemic stroke: an observational study
- PMID: 31496785
- PMCID: PMC6691961
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S213535
The expression of microRNA 146a in patients with ischemic stroke: an observational study
Abstract
Aim: We conducted the present prospective study to assess the level of microRNA (miRNA) 146a in patients with ischemic stroke and its correlation with patients' characteristics.
Methods: We conducted an observational study that included adult patients (≥18 years old) who presented within 24 hrs after the onset of the symptoms of acute ischemic stroke. In addition, age- and sex-matched healthy volunteers were included as control group. The primary outcome in the present study was the difference in miRNA 146a expression between patients with ischemic stroke and control group participants. The expression of miRNA 146a was measured using quantitative real-time PCR. Quantitative real-time PCR amplification and analysis were performed using Rotor-Gene Q thermal cycler.
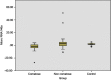
Results: The present study included 44 patients with ischemic stroke and 22 matched controls. Regarding the primary outcome of the present study, the median expression of miRNA 146a in patients with ischemic stroke was -1.98 fold (IQR -27.1-3.9) compared to 1.75 fold (IQR -2.25-5.27) in control group (P<0.001). However, the subgroup analysis showed that the expression of miRNA 146a was significantly downregulated in comatosed patients only (P<0.001). The expression of miRNA 146a correlated negatively with Glasgow Coma Scale score in comatose patients (r=-0.352, P=0.022).
Conclusion: In conclusion, the expression of miRNA 146a is significantly downregulated in ischemic stroke patients. Further studies are needed to assess its diagnostic utility and therapeutic potentials.
Keywords: cerebral infarction; coma; ischemic stroke; miRNA 146a.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources