Melatonin MT2 receptor agonist IIK-7 produces antinociception by modulation of ROS and suppression of spinal microglial activation in neuropathic pain rats
- PMID: 31496789
- PMCID: PMC6690853
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S214671
Melatonin MT2 receptor agonist IIK-7 produces antinociception by modulation of ROS and suppression of spinal microglial activation in neuropathic pain rats
Abstract
Background: In recent years, several melatonin (MLT) receptor agonists have been approved by FDA for the treatment of sleep disorders and depression. Very few studies have shed light on their efficacy against neuropathic pain (NP). IIK-7 is an MT-2 agonist known to promote sleep. Whether IIK-7 suppresses NP has not been reported, and the signaling profile is unknown.
Objective: To investigate the effect of melatonin type 2 receptor agonist IIK-7 on partial sciatic nerve transection-induced NP in rats and elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms.
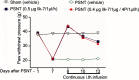
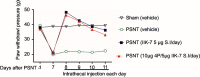
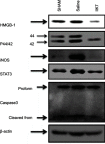
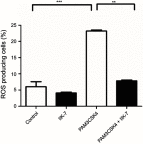
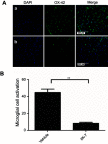
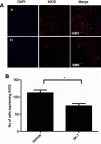
Methods: NP was induced by the PSNT in the left leg of adult male Wistar rats. On post-transection day 7, rats were implanted with intrathecal (i.t) catheter connected to an infusion pump and divided in to four groups: sham-operated/vehicle, PSNT/vehicle, PSNT/0.5 μg/hr IIK-7 and PSNT/0.5 μg IIK-7/1 μg 4-p/hr. To test the MT-2 dependence on IIK-7 activity, the animals were implanted with a single i.t catheter and injected MT-2 antagonist 4-Phenyl-2-propionamidotetralin (4-p) 20 mins prior to IIK-7 injection on day 7 after PSNT. The antinociceptive response was measured using a mechanical paw withdrawal threshold. Activation of microglial cells and the expression of NP-associated proteins in the spinal cord dorsal horn was assessed by immunofluorescence assay (IFA) and Western blotting (WB). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging ability of IIK-7 was evaluated by using bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM).
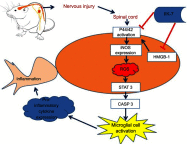
Results: Treatment with the MT-2 agonist IIK-7 significantly alleviated PSNT-induced mechanical allodynia and glial activation along with the inhibition of P44/42 MAPK, HMGB-1, STAT3, iNOS and casp-3 proteins.
Conclusion: IIK-7 attenuates NP through the suppression of glial activation and suppression of proteins involved in inflammation and apoptosis. MT-2 receptor agonists may establish a promising and unique therapeutic approach for the treatment of NP.
Keywords: IIK-7; MT-2 receptor; allodynia; neuropathic pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Kuthati Y, Lin S-H, Chen I-J, Wong C-S. Melatonin and their analogs as a potential use in the management of neuropathic pain. J Formos Med Assoc. 2018;118(8):1177–1186. doi:org/10.1016/j.jfma.2018.09.017 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

