The prognostic value of preoperative controlling nutritional status score in non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with surgery: a retrospective single-institution study
- PMID: 31496811
- PMCID: PMC6693320
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S209418
The prognostic value of preoperative controlling nutritional status score in non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with surgery: a retrospective single-institution study
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the significance of the controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score as a predictor for survival outcomes for non-metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients.
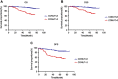
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 325 patients who received surgical treatment for renal cell carcinoma between 2010 and 2012 at Peking University First Hospital. Patients were divided into two groups according to the optimal cut-off value of CONUT score. Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test were used for survival analysis according to different CONUT groups. Cox proportional hazards regression models were performed to assess the prognostic value of clinicopathological parameters for overall survival (OS), cancer-specific survival (CSS) and disease-free survival (DFS) respectively.
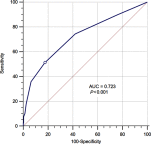
Results: The optimal cut-off value of CONUT score was 3. High CONUT score significantly correlated to higher tumor grade (P<0.001), later pathological T stage (P<0.001) and tumor necrosis (P<0.001). Patients with higher CONUT score had worse OS (HR 5.34, 95% CI 2.29-12.46, P<0.001), CSS (HR 5.51, 95% CI 2.12-14.33, P<0.001) and DFS (HR 4.23, 95% CI 2.16-8.29, P<0.001). In multivariable analysis, high CONUT score was an independent risk factor for OS, CSS and DFS (OS: HR=3.36, 95% CI 1.73-6.56, P<0.001; CSS: HR=3.34, 95% CI 1.59-6.98, P=0.001; DFS: HR=1.85, ]95% CI 1.07-3.21, P=0.029).
Conclusion: Preoperative CONUT score was an independent prognostic factor for OS, CSS and DFS in non-metastatic RCC patients treated with surgery.
Keywords: CONUT score; biomarker; renal cell carcinoma; surgery; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multicenter Study of Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as a Prognostic Factor in Patients With HIV-Related Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 30;12:778746. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.778746. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34917092 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the preoperative controlling nutritional status score as an independent predictor in a large Chinese cohort of patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2018 Dec;7(12):6112-6123. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1902. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 30485712 Free PMC article.
-
High Preoperative Controlling Nutritional Status Score Predicts a Poor Prognosis in Patients with Localized Upper Tract Urothelial Cancer: A Propensity Score Matching Study in a Large Chinese Center.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jan 15;12:323-335. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S225711. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32021446 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of the Controlling Nutritional Status score on patients undergoing nephrectomy for upper tract urothelial carcinoma or renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Nutr. 2022 Jul 28;128(2):217-224. doi: 10.1017/S0007114521002889. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Br J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34338171
-
Prognostic significance of pretreatment controlling nutritional status score in urological cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Feb 19;21(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01813-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33608012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The prognostic significance of controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score for surgically treated renal cell cancer and upper urinary tract urothelial cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Clin Nutr. 2022 Jun;76(6):801-810. doi: 10.1038/s41430-021-01014-0. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34815539
-
The Added Value of Controlling Nutritional Status (Conut) Score for Preoperative Counselling on Significant Early Loss of Renal Function After Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 17;16(20):3519. doi: 10.3390/cancers16203519. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456613 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of a combined and controlled nutritional status score and EBV-DNA in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a long-term follow-up study.Cancer Biol Med. 2021 Jun 16;19(4):551-64. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0627. Online ahead of print. Cancer Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34132505 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter Study of Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as a Prognostic Factor in Patients With HIV-Related Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 30;12:778746. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.778746. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34917092 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of the Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score in surgically treated breast cancer patients.Gland Surg. 2020 Oct;9(5):1370-1379. doi: 10.21037/gs-20-294. Gland Surg. 2020. PMID: 33224812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Semeniuk-Wojtas A, Lubas A, Stec R, Syrylo T, Niemczyk S, Szczylik C. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and c-reactive protein as new and simple prognostic factors in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018;16(3):e685–e693. doi:10.1016/j.clgc.2018.01.010 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

