The Purinome and the preBötzinger Complex - A Ménage of Unexplored Mechanisms That May Modulate/Shape the Hypoxic Ventilatory Response
- PMID: 31496935
- PMCID: PMC6712068
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00365
The Purinome and the preBötzinger Complex - A Ménage of Unexplored Mechanisms That May Modulate/Shape the Hypoxic Ventilatory Response
Abstract
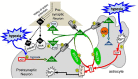
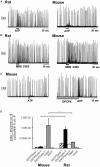
Exploration of purinergic signaling in brainstem homeostatic control processes is challenging the traditional view that the biphasic hypoxic ventilatory response, which comprises a rapid initial increase in breathing followed by a slower secondary depression, reflects the interaction between peripheral chemoreceptor-mediated excitation and central inhibition. While controversial, accumulating evidence supports that in addition to peripheral excitation, interactions between central excitatory and inhibitory purinergic mechanisms shape this key homeostatic reflex. The objective of this review is to present our working model of how purinergic signaling modulates the glutamatergic inspiratory synapse in the preBötzinger Complex (key site of inspiratory rhythm generation) to shape the hypoxic ventilatory response. It is based on the perspective that has emerged from decades of analysis of glutamatergic synapses in the hippocampus, where the actions of extracellular ATP are determined by a complex signaling system, the purinome. The purinome involves not only the actions of ATP and adenosine at P2 and P1 receptors, respectively, but diverse families of enzymes and transporters that collectively determine the rate of ATP degradation, adenosine accumulation and adenosine clearance. We summarize current knowledge of the roles played by these different purinergic elements in the hypoxic ventilatory response, often drawing on examples from other brain regions, and look ahead to many unanswered questions and remaining challenges.
Keywords: P1 receptor; P2 receptor; adenosine kinase; ectonucleotidase; equilibrative nucleoside transporter; hypoxia.
Figures


References
-
- Abbracchio M. P., Brambilla R., Ceruti S., Kim H. O., von Lubitz D. K., Jacobson K. A., et al. (1995). G protein-dependent activation of phospholipase C by adenosine A3 receptors in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 48 1038–1045. - PubMed
-
- Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G., Boeynaems J. M., Barnard E. A., Boyer J. L., Kennedy C., et al. (2006). International union of pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 58 281–341. 10.1124/pr.58.3.3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

