Identification of an ERK Inhibitor as a Therapeutic Drug Against Tau Aggregation in a New Cell-Based Assay
- PMID: 31496937
- PMCID: PMC6712076
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00386
Identification of an ERK Inhibitor as a Therapeutic Drug Against Tau Aggregation in a New Cell-Based Assay
Abstract
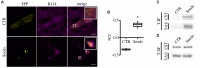
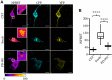
Formation of Tau aggregates is a common pathological feature of tauopathies and their accumulation directly correlates with cytotoxicity and neuronal degeneration. Great efforts have been made to understand Tau aggregation and to find therapeutics halting or reversing the process, however, progress has been slowed due to the lack of a suitable method for monitoring Tau aggregation. We developed a cell-based assay allowing to detect and quantify Tau aggregation in living cells. The system is based on the FRET biosensor CST able to monitor the molecular dynamic of Tau aggregation in different cellular conditions. We probed candidate compounds that could block Tau hyperphosphorylation. In particular, to foster the drug discovery process, we tested kinase inhibitors approved for the treatment of other diseases. We identified the ERK inhibitor PD-901 as a promising therapeutic molecule since it reduces and prevents Tau aggregation. This evidence establishes the CST cell-based aggregation assay as a reliable tool for drug discovery and suggests that PD-901 might be a promising compound to be tested for further preclinical studies on AD.
Keywords: CST; ERK; FRET; Tau; Tau biosensor; aggregation.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

