Combination of Cannabinoids, Δ9- Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol, Ameliorates Experimental Multiple Sclerosis by Suppressing Neuroinflammation Through Regulation of miRNA-Mediated Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 31497013
- PMCID: PMC6712515
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01921
Combination of Cannabinoids, Δ9- Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol, Ameliorates Experimental Multiple Sclerosis by Suppressing Neuroinflammation Through Regulation of miRNA-Mediated Signaling Pathways
Abstract
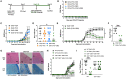
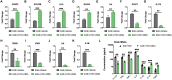
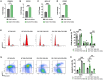
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic and disabling disorder of the central nervous system (CNS) characterized by neuroinflammation leading to demyelination. Recently a combination of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD) extracted from Cannabis has been approved in many parts of the world to treat MS-related spasticity. THC+CBD combination was also shown to suppresses neuroinflammation, although the mechanisms remain to be further elucidated. In the current study, we demonstrate that THC+CBD combination therapy (10 mg/kg each) but not THC or CBD alone, attenuates murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) by reducing neuroinflammation and suppression of Th17 and Th1 cells. These effects were mediated through CB1 and CB2 receptors inasmuch as, THC+CBD failed to ameliorate EAE in mice deficient in CB1 and CB2. THC+CBD treatment also caused a decrease in the levels of brain infiltrating CD4+ T cells and pro-inflammatory molecules (IL-17, INF-γ, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and TBX21), while increasing anti-inflammatory phenotype such as FoxP3, STAT5b, IL-4, IL-10, and TGF-β. Also, the brain-derived cells showed increased apoptosis along with decreased percentage in G0/G1 phase with increased percentage in G2/M phase of cell cycle. miRNA microarray analysis of brain-derived CD4+ T cells revealed that THC+CBD treatment significantly down-regulated miR-21a-5p, miR-31-5p, miR-122-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-150-5p, miR-155-5p, and miR-27b-5p while upregulating miR-706-5p and miR-7116. Pathway analysis showed that majority of the down-regulated miRs targeted molecules involved in cycle arrest and apoptosis such as CDKN2A, BCL2L11, and CCNG1, as well as anti-inflammatory molecules such as SOCS1 and FoxP3. Additionally, transfection studies involving miR-21 and use of Mir21-/- mice suggested that while this miR plays a critical role in EAE, additional miRs may also be involved in THC+CBD-mediated attenuation of EAE. Collectively, this study suggests that combination of THC+CBD suppresses neuroinflammation and attenuates clinical EAE development and that this effect is associated with changes in miRNA profile in brain-infiltrating cells.
Keywords: CB1; CB2; CBD; EAE; THC; miR-21a-5p; multiple sclerosis.
Figures
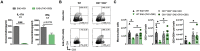

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

