Peri-procedural hemostasis disorders in surgical and transcatheter aortic valve implantation
- PMID: 31497050
- PMCID: PMC6727236
- DOI: 10.5114/aic.2019.83649
Peri-procedural hemostasis disorders in surgical and transcatheter aortic valve implantation
Abstract
Introduction: Despite their high effectiveness, surgical aortic valve replacement (AVR) and transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) are associated with substantial risk of bleeding. Although procedure-related hemostasis disorders might be crucial for safety of both procedures, the amount of data on the peri-procedural status of hemostasis in patients with aortic valve stenosis (AS) subjected to AVR and TAVI is negligible.
Aim: To investigate the profile of peri-procedural hemostasis in elderly patients with AS, subjected to aortic valve prosthesis implantation.
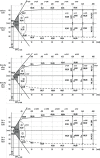
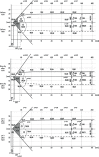
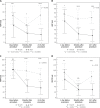
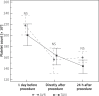
Material and methods: We performed a prospective analysis of global hemostasis using ROTEM thromboelastometry and platelet reactivity assessment using impedance aggregometry in 30 consecutive patients ≥ 70 years old subjected to AVR and TAVI. All tests were performed within 24 h before, directly and 24 h after the procedures.
Results: Surgical aortic valve replacement was characterized by transient hypofibrinogenemia and von Willebrand factor (vWF) depletion, which quickly recovered within 24 h after AVR. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation was characterized by substantial alteration of platelet function and vWF depletion with significant platelet reactivity impairment and increase in platelet sensitivity to antiplatelet agent, early after the procedure. TAVI-related hemostasis alterations were not recovered at 24 h after the procedure.
Conclusions: Surgical and transcatheter aortic valve replacement procedures are associated with substantial and diverse peri-procedural hemostasis disorders. Since hemostasis disorders related to TAVI are mainly characterized by impaired platelet function, early dual antiplatelet prophylaxis after TAVI requires careful consideration.
Keywords: aortic valve replacement; bleeding complications; peri-procedural hemostasis disorders; platelet reactivity; transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pre-procedural abnormal function of von Willebrand Factor is predictive of bleeding after surgical but not transcatheter aortic valve replacement.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2019 Nov;48(4):610-618. doi: 10.1007/s11239-019-01917-7. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2019. PMID: 31359325 Free PMC article.
-
Correction of acquired von Willebrand syndrome by transcatheter aortic valve implantation.J Invasive Cardiol. 2014 Dec;26(12):654-8. J Invasive Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25480995
-
The role of platelet reactivity assessment in dual antiplatelet prophylaxis after transcatheter aortic valve implantation.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2018 Apr;111(4):233-245. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 29126843
-
Peri-procedural thrombocytopenia after aortic bioprosthesis implant: A systematic review and meta-analysis comparison among conventional, stentless, rapid-deployment, and transcatheter valves.Int J Cardiol. 2019 Dec 1;296:43-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.07.056. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Int J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31351790
-
Direct and adjusted indirect comparisons of perioperative mortality after sutureless or rapid-deployment aortic valve replacement versus transcatheter aortic valve implantation.Int J Cardiol. 2017 Feb 1;228:327-334. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.11.253. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27866023 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of aortic valve replacement in Heyde syndrome: a meta-analysis.Eur Heart J. 2023 Sep 1;44(33):3168-3177. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad340. Eur Heart J. 2023. PMID: 37555393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Le Tourneau T, Breyne J, Susen S. Ambivalent effect of aortic stenosis on von Willebrand factor and thrombin generation. Is transvalvular gradient the guilty party? Heart. 2011;97:1997–8. - PubMed
-
- Natorska J, Bykowska K, Hlawaty M, et al. Increased thrombin generation and platelet activation are associated with deficiency in high molecular weight multimers of von Willebrand factor in patients with moderate-to-severe aortic stenosis. Heart. 2011;97:2023–8. - PubMed
-
- Badar ER, Gremmel T, Schneller A, et al. High levels of platelet-monocyte aggregates after valve replacement for aortic stenosis: relation to soluble P-selectin and P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 genes. Thrombosis Res. 2012;129:453–8. - PubMed
-
- Chirkov YY, Holmes AS, Willoughby SR, et al. Association of aortic stenosis with platelet hyperaggregability and impaired responsiveness to nitric oxide. Am J Cardiol. 2002;90:551–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
