Prenatal diagnosis of Pallister-Killian syndrome using cord blood samples
- PMID: 31497069
- PMCID: PMC6717365
- DOI: 10.1186/s13039-019-0449-x
Prenatal diagnosis of Pallister-Killian syndrome using cord blood samples
Abstract
Background: Pallister-Killian syndrome (PKS) (OMIM:#601803) is a rare sporadic genetic disorder characterized by multi-malformations which is caused by the presence of the extra isochromosome 12p. PKS is featured by the tissue-limited mosaicism of the isochromosome 12p [i(12p)]. There were a wide spectrum of prenatal ultrasound findings of PKS, which made it difficult to be found in first or second trimester. Polyhydramnios, diaphragmatic hernia, and rhizomelic limb shortening were the most common prenatal ultrasound abnormalities in PKS. This study retrospectively analyzed the ultrasound findings and molecular cytogenetic results of four PKS fetuses diagnosed by using cord blood samples.
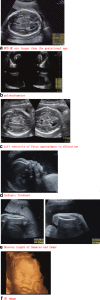
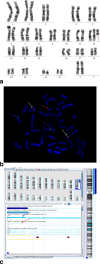
Results: The ultrasound anomalies of four PKS fetuses are described as follows: fetal macrosomia, cerebral ventriculomegaly, increased NT thickness, rhizomelic limbs shortening, polyhydramnios. Biparietal diameter (BPD), head circumference (HC), abdominal circumference (AC), femur length (FL) measurements were above the mean in three fetuses,while one fetus showed rhizomelic limbs shortening. Combined with this study and previous literature, polyhydramnios was the most frequent anomaly observed in prenatal ultrasound examination of PKS, which accounted for 48% (94/194). Fetal macrosomia was present in 15% (29/194), cerebral ventriculomegaly in 13% (25/194), thickened nuchal fold in 9% (18/194), rhizomelic limbs shortening in 26% (51/194). I(12p) was found in the karyotype analysis of cultured cord blood lymphocytes and the mosaic ratios ranged from 2 to 5%. Single nucleotide polymorphisms array (SNP-array) results suggested that the whole short arm of chromosome 12 was duplicated with 2~3 copies. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed to confirm the results of karyotype and SNP-array.
Conclusions: In case non-specific indicators such as fetal macrosomia, polyhydramnios and rhizomelic limbs shortening are observed meanwhile in prenatal ultrasound, targeted detection of PKS should be considered. In the prenatal diagnosis of PKS, the combination of SNP-array and FISH with conventional karyotype are the key to seek i(12p) and for precise diagnosis.
Keywords: Cord blood; Isochromosome 12p; Pallister-Killian syndrome; Prenatal diagnosis; Ultrasound findings.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Schubert Regine, Viersbach Renate, Eggermann Thomas, Hansmann Manfred, Schwanitz Gesa. Report of two new cases of Pallister-Killian syndrome confirmed by FISH: Tissue-specific mosaicism and loss of i(12p) by in vitro selection. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 1997;72(1):106–110. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19971003)72:1<106::AID-AJMG21>3.0.CO;2-U. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Salzano E, Raible SE, Kaur M, Wilkens A, Sperti G, Tilton RK, Bettini LR, Rocca A, Cocchi G, Selicorni A, Conlin LK, McEldrew D, Gupta R, Thakur S, Izumi K, Krantz ID. Prenatal profile of Pallister-Killian syndrome: Retrospective analysis of 114 pregnancies, literature review and approach to prenatal diagnosis. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A. 2018;176(12):2575–2586. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.40499. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

