The evolving immuno-oncology landscape in advanced lung cancer: first-line treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 31497071
- PMCID: PMC6716180
- DOI: 10.1177/1758835919870360
The evolving immuno-oncology landscape in advanced lung cancer: first-line treatment of non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Lung cancer is the most common cancer and leading cause of cancer death. While targeted therapies have redefined treatment options for non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) with genetic aberrations such as epidermal growth factor and anaplastic lymphoma kinase, many patients do not harbour these oncogenic drivers. Cancer immunology has enabled the development of immune modulators that has dramatically altered the therapeutic landscape of advanced NSCLC. The success of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in pretreated NSCLC has led to the conduct of multiple studies exploring their role in the first-line setting. This article provides an overview of the evolving landscape of immune-checkpoint inhibitors with a focus on the programmed cell-death 1 (PD-1; pembrolizumab, nivolumab) and programmed cell-death ligand 1 (PD-L1; atezolizumab, durvalumab, avelumab) immune-checkpoint inhibitors as single agent or in combination with either chemotherapy or with another immune-checkpoint inhibitor in the treatment of NSCLC, the challenges faced, as well as future perspectives.
Keywords: anti-PD-1; anti-PD-L1; chemotherapy; combination immunotherapy; immunotherapy; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: RAS has received honoraria from Astra-Zeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Taiho, Takeda, and Yuhan; and research funding from Astra-Zeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim. The other authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
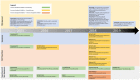
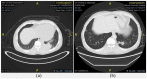
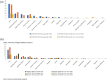
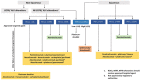
References
-
- World Health Organization. Cancer, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (2018, accessed 4 May 2019).
-
- Cancer.Net. Lung cancer - non-small cell: statistics, https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/lung-cancer-non-small-cell/statistics (2019, accessed 4 May 2019).
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000; 100: 57–70. - PubMed
-
- Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ. The B7-CD28 superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol 2002; 2: 116–126. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

