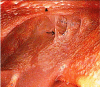
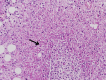
Tissue Xpert® MTB/RIF Assay in Peritoneal Tuberculosis: To be (Done) or Not to be (Done)
- PMID: 31497439
- PMCID: PMC6713244
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.5009
Tissue Xpert® MTB/RIF Assay in Peritoneal Tuberculosis: To be (Done) or Not to be (Done)
Abstract
Introduction Peritoneal tuberculosis (PTB) is a paucibacillary disease with poor mycobacterial yield in ascitic fluid. The Xpert® MTB/RIF assay (Gene Xpert) is a new tool for the diagnosis of tuberculosis (TB) and has not yet been studied on peritoneal tissue. The present study aimed to investigate the yield of the Xpert® MTB/RIF assay on peritoneal tissue obtained at peritoneoscopy. Methods This is a retrospective study and the data were collected from hospital records. The patients who underwent peritoneoscopy along with Xpert® MTB/RIF assay on peritoneal tissue were included in this study. Those with proven PTB were considered as cases while those with other diagnoses as controls. Using the reference standard of TB diagnosis, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of Xpert® MTB/RIF assay were calculated. Results Total of 36 patients was analyzed in this study: 28 as cases and eight as controls. Peritoneoscopy was carried out for diagnosis and biopsy. Histopathology in cases revealed caseating granulomas in 16 while 11 had non-caseating granulomas. Nine patients showed acid-fast bacillus positivity on peritoneal tissue. The most common finding on peritoneoscopy was tubercles with adhesions (n = 14, 50%), followed by tubercles only (n = 12, 42.9%). Xpert® MTB/RIF assay was positive in 17 (60.7%) patients with a sensitivity of 60.71%, specificity of 100%, and an accuracy of 69.44%. Two patients expressed rifampicin resistance. Conclusion Xpert® MTB/RIF assay on peritoneal tissue has fair sensitivity and excellent specificity. The multidrug resistance and the ability to provide results rapidly make it clinically useful.
Keywords: abdominal tuberculosis; diagnostic laparoscopy; gene xpert; peritonitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Khuroo MS, Khuroo NS. In Tuberculosis. Vol. 1. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2004. Abdominal tuberculosis; pp. 659–667.
-
- Systematic review: tuberculous peritonitis - presenting features, diagnostic strategies and treatment. Sanai FM, Bzeizi KI. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005;22:685–700. - PubMed
-
- Diagnostic value of adenosine deaminase in ascites for tuberculosis ascites: a meta-analysis. Tao L, Ning H-J, Nie H-M, Guo X-Y, Qin S-Y, Jiang H-X. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;79:102–107. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources