Mechanism of Probiotic VSL#3 Inhibiting NF-κB and TNF-α on Colitis through TLR4-NF-κB Signal Pathway
- PMID: 31497551
- PMCID: PMC6708536
Mechanism of Probiotic VSL#3 Inhibiting NF-κB and TNF-α on Colitis through TLR4-NF-κB Signal Pathway
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the effect of probiotic VSL#3 on NF-κB and TNF-α in rats with colitis and the correlation with TLR4-NF-κB signal pathway.
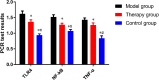
Methods: Sixty Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were divided into the control, model and therapy groups (n=20) according to the random number table. Rats in the model and therapy groups were modeled for colitis, and rats in the therapy group were intragastrically administered with probiotic VSL#3. The expression of TLR4 and NF-κB protein, and the levels of NF-κB, TLR4, and TNF-α mRNA in the colon tissue were detected. The concentration of TNF-α in the serum after modeling but before intragastric administration (T0), 3d (T1) and 7d after intragastric administration (T2) was detected.
Results: The expression of TLR4 and NF-κB p65 protein, and the levels of TLR4, NF-κB, and TNF-α mRAN in the therapy group decreased (P < 0.001). At T0, T1, and T2, the concentration of TNF-α in the model and control groups increased (P < 0.001). TLR4 and NF-κB in the therapy group were positively correlated with TNF-α mRAN (P < 0.050).Conclusion: In conclusion, probiotic VSL#3 inhibits the expression of NF-κB and TNF-α in rats with colitis through TLR4-NF-κB signal pathway, so it is expected to be a first choice drug for the treatment of colitis.
Conclusion: In conclusion, probiotic VSL#3 inhibits the expression of NF-κB and TNF-α in rats with colitis through TLR4-NF-κB signal pathway, so it is expected to be a first choice drug for the treatment of colitis.
Keywords: NF-κB; Probiotics VSL#3; TLR4; TNF-α.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The anti-inflammation effect of baicalin on experimental colitis through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB pathway activation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Nov;23(1):294-303. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.09.005. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25239813
-
VSL#3 probiotics exerts the anti-inflammatory activity via PI3k/Akt and NF-κB pathway in rat model of DSS-induced colitis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Feb;374(1-2):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1488-3. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23271629
-
[β1 receptor blocker decreases the myocardial inflammation in the sepsis adult rats through inhibition of TLR4/NF-ΚB signaling pathway].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Feb;31(2):193-197. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.02.014. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 30827308 Chinese.
-
[Effect of moxibustion on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in colon of diarrhea-predo-minant irritable bowel syndrome rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020 Aug 25;45(8):633-9. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.190950. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2020. PMID: 32869573 Chinese.
-
[Effect of Xuebijing Injection on TLR4-NF-κB-TNF-α pathway of rats' myocardial anoxia/reoxygenation].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2014 Dec;34(12):1463-8. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25632747 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Yeast Fermentate Prebiotic Ameliorates Allergic Asthma, Associating with Inhibiting Inflammation and Reducing Oxidative Stress Level through Suppressing Autophagy.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Jan 19;2021:4080935. doi: 10.1155/2021/4080935. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 33542675 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Influenced by Postbiotics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 15;22(24):13475. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413475. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probiotics: a promising future in the treatment of ulcerative colitis?Pharmacol Rep. 2025 Jun;77(3):645-657. doi: 10.1007/s43440-025-00724-7. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Pharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40214948 Review.
-
Gut instinct: harnessing the power of probiotics to tame pathogenic signaling pathways in ulcerative colitis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 11;11:1396789. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1396789. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39323474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probiotics: A potential immunomodulator in COVID-19 infection management.Nutr Res. 2021 Mar;87:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2020.12.014. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Nutr Res. 2021. PMID: 33592454 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fumery M, Kohut M, Gower-Rousseau C, et al. (2017). Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Associated Factors of Microscopic Colitis in Northern France: A Population-Based Study. Dig Dis Sci, 62: 1571–1579. - PubMed
-
- Pardi DS. (2017). Diagnosis and Management of Microscopic Colitis. Am J Gastroenterol, 112: 78–85. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
