Detection and Characterization of Catechol Quinone-Derived Protein Adducts Using Biomolecular Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 31497592
- PMCID: PMC6712063
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00571
Detection and Characterization of Catechol Quinone-Derived Protein Adducts Using Biomolecular Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
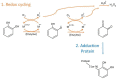
The catechol quinone (CQ) motif is present in many biologically relevant molecules throughout endogenous metabolic products, foods, drugs, and environmental pollutants. The CQ derivatives may undergo Michael addition, and has been shown to yield covalent bonds with nucleophilic sites of cysteine, lysine, or histidine residue of proteins. The CQ-adducted proteins may exhibit cytotoxicity or biological functions different from their un-adducted forms. Identification, characterization, and quantification of relevant protein targets are essential but challenging goals. Mass spectrometry (MS) is well-suited for the analysis of proteins and protein modifications. Technical development of bottom-up proteomics has greatly advanced the field of biomolecular MS, including protein adductomics. This mini-review focuses on the use of biomolecular MS in (1) structural and functional characterization of CQ adduction on standards of proteins, (2) identification of endogenous adduction targets, and (3) quantification of adducted blood proteins as exposure index. The reactivity and outcome of CQ adduction are discussed with emphases on endogenous species, such as dopamine and catechol estrogens. Limitations and advancements in sample preparation, MS instrumentation, and software to facilitate protein adductomics are also discussed.
Keywords: adductomics; biomolecular mass spectrometry; catechol; catechol quinone; parallel reaction monitoring; protein adduction; quinone; selective reaction monitoring.
Figures
References
-
- Bolton J. L., Shen L. (1996). p-Quinone methides are the major decomposition products of catechol estrogen o-quinones. Carcinogenesis 17, 925–929. - PubMed
-
- Cavalieri E., Chakravarti D., Guttenplan J., Hart E., Ingle J., Jankowiak R., et al. (2006). Catechol estrogen quinones as initiators of breast and other human cancers: implications for biomarkers of susceptibility and cancer prevention. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1766, 63–78. 10.1016/j.bbcan.2006.03.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources