Omics Application of Bio-Hydrogen Production Through Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- PMID: 31497598
- PMCID: PMC6712067
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00201
Omics Application of Bio-Hydrogen Production Through Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
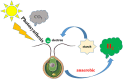
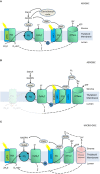
This article summarizes the current knowledge regarding omics approaches, which include genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics, in the context of bio-hydrogen production in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. In this paper, critical genes (HydA1, Hyd A2, Sulp, Tla1, Sta7, PFL1) involved in H2 metabolism were identified and analyzed for their function in H2 accumulation. Furthermore, the advantages of gene microarrays and RNA-seq were compared, as well as their applications in transcriptomic analysis of H2 production. Moreover, as a useful tool, proteomic analysis could identify different proteins that participate in H2 metabolism. This review provides fundamental theory and an experimental basis for H2 production, and further research effort is needed in this field.
Keywords: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; genomics; hydrogen production; metabolomics; proteomics; transcriptomics.
Figures
References
-
- Antal T. K., Krendeleva T. E., Laurinavichene T. V., Makarova V. V., Ghirardi M. L., Rubin A. B., et al. (2003). The dependence of algal H2 production on photosystem II and O2-consumption activity in sulfur-deprived Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1607, 153–160. 10.1016/j.bbabio.2003.09.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boichenko V. A., Greenbaum E., Seibert M. (2004). Hydrogen production by photosynthetic microorganisms. Mol. Glob. Photosynt. 2, 397–451. 10.1142/9781860945496_0008 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources