Bilateral benign reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the conjunctiva: a case treated with oral doxycycline and review of the literature
- PMID: 31497614
- PMCID: PMC6717973
- DOI: 10.1186/s40662-019-0151-4
Bilateral benign reactive lymphoid hyperplasia of the conjunctiva: a case treated with oral doxycycline and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: To report a case of bilateral benign reactive lymphoid hyperplasia (BRLH) of the conjunctiva treated with oral doxycycline and perform review of the literature evaluating the presentation, treatment and risk of transformation to lymphoma.
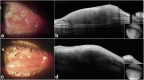
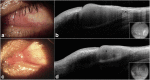
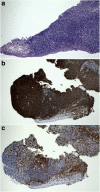
Case presentation: A case report is described and review of the literature from January 1975 to January 2019 was performed. A 30-year-old man presented with bilateral enlarging fleshy pink medial canthal conjunctival lesions. Incisional biopsy revealed BRLH. Oral doxycycline was initiated (100 mg two times a day) for a total of 2 months. Both lesions decreased in size significantly at the patient's two-month follow up visit. The residual lesion in the right eye was excised along with an adjacent pterygium and the patient has been free of recurrence for the past 1.5 years. The lesion in the left eye has remained stable in size after cessation of the oral doxycycline. A total of 235 cases of conjunctival BRLH were identified in our literature search. The mean age at diagnosis was 35.2 years (range, 5 to 91 years). BRLH lesions were unilateral in 75% of patients and bilateral in 25% of them. Seven patients (2.9%) had a concurrent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection at the time of lesion appearance. The most common treatments were surgical excision (155/235 or 65.9%) and corticosteroids (30/235 or 12.7%), while 14% (33/235) of the patients were observed and 4.6% (11/235) received external beam radiotherapy alone. Recurrence occurred in ten patients (10/235 or 4.2%), of whom five had undergone surgical excision alone, two excision followed by external beam radiotherapy, one excision and oral corticosteroids, one radiotherapy alone and one had been treated with topical corticosteroids. Overall, only 2 of the 235 reported cases (0.8%) developed malignancy, one localized to the conjunctiva and one systemic.
Conclusions: Benign reactive lymphoid hyperplasia is one of the lymphoproliferative disorders of the conjunctiva and ocular adnexa. Extensive literature review shows that most cases are treated with surgery, steroids or observation. Oral doxycycline may be considered an alternative non-invasive treatment of BRLH conjunctival lesions. BRLH lesions warrant careful follow up as they can rarely transform into conjunctival or systemic lymphoma.
Keywords: Atypical lymphoid hyperplasia; Conjunctival biopsy; Conjunctival lymphoid lesion; Conjunctival lymphoma; Conjunctival tumor; High resolution anterior segment optical coherence tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Shields CL, Shields JA, Carvalho C, Rundle P, Smith AF. Conjunctival lymphoid tumors: clinical analysis of 117 cases and relationship to systemic lymphoma. Ophthalmology. 2001;108(5):979–984. - PubMed
-
- Coupland SE, Krause L, Delecluse HJ, Anagnostopoulos I, Foss HD, Hummel M, et al. Lymphoproliferative lesions of the ocular adnexa. Analysis of 112 cases. Ophthalmology. 1998;105(8):1430–1441. - PubMed
-
- Sharara N, Holden JT, Wojno TH, Feinberg AS, Grossniklaus HE. Ocular adnexal lymphoid proliferations: clinical, histologic, flow cytometric, and molecular analysis of forty-three cases. Ophthalmology. 2003;110(6):1245–1254. - PubMed
-
- Stacy Rebecca C., Jakobiec Frederick A., Schoenfield Lynn, Singh Arun D. Unifocal and Multifocal Reactive Lymphoid Hyperplasia vs Follicular Lymphoma of the Ocular Adnexa. American Journal of Ophthalmology. 2010;150(3):412-426.e1. - PubMed
-
- McLeod SD, Edward DP. Benign lymphoid hyperplasia of the conjunctiva in children. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999;117(6):832–835. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

