Data in support of genetic architecture of glucosinolate variations in Brassica napus
- PMID: 31497635
- PMCID: PMC6722234
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2019.104402
Data in support of genetic architecture of glucosinolate variations in Brassica napus
Abstract
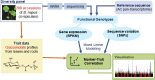
The transcriptome-based GWAS approach, Associative Transcriptomics (AT), which was employed to uncover the genetic basis controlling quantitative variation of glucosinolates in Brassica napus vegetative tissues is described. This article includes the phenotypic data of leaf and root glucosinolate (GSL) profiles across a diversity panel of 288 B. napus genotypes, as well as information on population structure and levels of GSLs grouped by crop types. Moreover, data on genetic associations of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers and gene expression markers (GEMs) for the major GSL types are presented in detail, while Manhattan plots and QQ plots for the associations of individual GSLs are also included. Root genetic association are supported by differential expression analysis generated from root RNA-seq. For further interpretation and details, please see the related research article entitled 'Genetic architecture of glucosinolate variation in Brassica napus' (Kittipol et al., 2019).
Keywords: Associative transcriptomics; Brassica napus; Gene expression markers; Genetic associations; Glucosinolates; Oilseed rape; Population structure; SNP markers.
Figures

References
-
- Havlickova L., He Z., Wang L., Langer S., Harper A.L., Kaur H., Broadley M.R., Gegas V., Bancroft I. Validation of an updated Associative Transcriptomics platform for the polyploid crop species Brassica napus by dissection of the genetic architecture of erucic acid and tocopherol isoform variation in seeds. Plant J. 2018;93:181–192. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harper A.L., Trick M., Higgins J., Fraser F., Clissold L., Wells R., Hattori C., Werner P., Bancroft I. Associative transcriptomics of traits in the polyploid crop species Brassica napus. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012;30:798–802. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

