A Therapeutic Silencing RNA Targeting Hepatocyte TAZ Prevents and Reverses Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice
- PMID: 31497743
- PMCID: PMC6719739
- DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1405
A Therapeutic Silencing RNA Targeting Hepatocyte TAZ Prevents and Reverses Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice
Erratum in
-
Correction.Hepatol Commun. 2019 Nov 26;4(1):134. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1455. eCollection 2020 Jan. Hepatol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31909361 Free PMC article.
Abstract
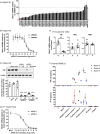
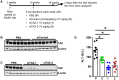
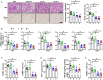
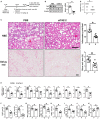
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is emerging as a major public health issue and is associated with significant liver-related morbidity and mortality. At present, there are no approved drug therapies for NASH. The transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ; encoded by WW domain-containing transcription regulator 1 [WWTR1]) is up-regulated in hepatocytes in NASH liver from humans and has been shown to causally promote inflammation and fibrosis in mouse models of NASH. As a preclinical test of targeting hepatocyte TAZ to treat NASH, we injected stabilized TAZ small interfering RNA (siRNA) bearing the hepatocyte-specific ligand N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc-siTAZ) into mice with dietary-induced NASH. As a preventative regimen, GalNAc-siTAZ inhibited inflammation, hepatocellular injury, and the expression of profibrogenic mediators, accompanied by decreased progression from steatosis to NASH. When administered to mice with established NASH, GalNAc-siTAZ partially reversed hepatic inflammation, injury, and fibrosis. Conclusion: Hepatocyte-targeted siTAZ is potentially a novel and clinically feasible treatment for NASH.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of Fibrosis Development in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Gastroenterology. 2020 May;158(7):1913-1928. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.311. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Gastroenterology. 2020. PMID: 32044315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocyte-targeted siTAZ therapy lowers liver fibrosis in NASH diet-fed chimeric mice with hepatocyte-humanized livers.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2023 Nov 23;31:101165. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2023.101165. eCollection 2023 Dec 14. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2023. PMID: 38144682 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte TAZ/WWTR1 Promotes Inflammation and Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Cell Metab. 2016 Dec 13;24(6):848-862. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.016. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Cell Metab. 2016. PMID: 28068223 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte-specific TAZ deletion downregulates p62/ Sqstm1 expression in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 8;535:60-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.12.038. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33341674
-
Targeting FGF21 for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Mar;41(3):199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.12.005. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31980251 Review.
Cited by
-
TAZ-induced Cybb contributes to liver tumor formation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.J Hepatol. 2022 Apr;76(4):910-920. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.031. Epub 2021 Dec 11. J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 34902531 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Fibrosis Development in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Gastroenterology. 2020 May;158(7):1913-1928. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.311. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Gastroenterology. 2020. PMID: 32044315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-33 deletion in hepatocytes attenuates MASLD-MASH-HCC progression.JCI Insight. 2024 Aug 27;9(19):e168476. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.168476. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39190492 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): pathomechanisms and pharmacotherapies.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Sep 6;18(15):5681-5697. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.65044. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36263163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivery of Oligonucleotides to the Liver with GalNAc: From Research to Registered Therapeutic Drug.Mol Ther. 2020 Aug 5;28(8):1759-1771. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.06.015. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32592692 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Corey KE, Kaplan LM. Obesity and liver disease: the epidemic of the twenty‐first century. Clin Liver Dis 2014;18:1‐18. - PubMed
-
- Rinella ME. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. JAMA 2015;313:2263‐2273. - PubMed
-
- Kabbany MN, Conjeevaram Selvakumar PK, Watt K, Lopez R, Akras Z, Zein N, et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis‐associated cirrhosis in the United States: an analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data. Am J Gastroenterol 2017;112:581‐587. - PubMed
-
- Estes C, Anstee QM, Arias‐Loste MT, Bantel H, Bellentani S, Caballeria J, et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016‐2030. J Hepatol 2018;69:896‐904. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

