Data-Driven Approach to Multiple-Source Domain Adaptation
- PMID: 31497777
- PMCID: PMC6730632
Data-Driven Approach to Multiple-Source Domain Adaptation
Abstract
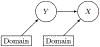
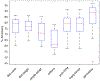
A key problem in domain adaptation is determining what to transfer across different domains. We propose a data-driven method to represent these changes across multiple source domains and perform unsupervised domain adaptation. We assume that the joint distributions follow a specific generating process and have a small number of identifiable changing parameters, and develop a data-driven method to identify the changing parameters by learning low-dimensional representations of the changing class-conditional distributions across multiple source domains. The learned low-dimensional representations enable us to reconstruct the target-domain joint distribution from unlabeled target-domain data, and further enable predicting the labels in the target domain. We demonstrate the efficacy of this method by conducting experiments on synthetic and real datasets.
Figures


References
-
- Zhang Kun, Bernhard Schölkopf Krikamol Muandet, and Wang Zhikun. Domain adaptation under target and conditional shift In ICML (3), pages 819–827, 2013.
-
- Zhang Kun, Gong Mingming, and Bernhard Schölkopf. Multi-source domain adaptation: A causal view In AAAI, pages 3150–3157, 2015.
-
- Pearl J. Causality: Models, Reasoning, and Inference. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000.
-
- Spirtes P, Glymour C, and Scheines R. Causation, Prediction, and Search. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 2nd edition, 2001.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
