Delayed intervention with a novel SGLT2 inhibitor NGI001 suppresses diet-induced metabolic dysfunction and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice
- PMID: 31497874
- PMCID: PMC6989948
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14859
Delayed intervention with a novel SGLT2 inhibitor NGI001 suppresses diet-induced metabolic dysfunction and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, is closely related to metabolic diseases such as obesity and diabetes. Despite an accumulating number of studies, no pharmacotherapy that targets NAFLD has received general approval for clinical use.
Experimental approach: Inhibition of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) is a promising approach to treat diabetes, obesity, and associated metabolic disorders. In this study, we investigated the effect of a novel SGLT2 inhibitor, NGI001, on NAFLD and obesity-associated metabolic symptoms in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mice.
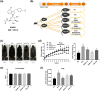
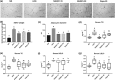
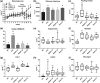
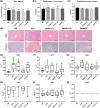
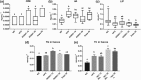
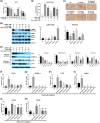
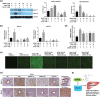
Key results: Delayed intervention with NGI001 protected against body weight gain, hyperglycaemia, hyperlipidaemia, and hyperinsulinaemia, compared with HFD alone. Adipocyte hypertrophy was prevented by administering NGI001. NGI001 inhibited impaired glucose metabolism and regulated the secretion of adipokines associated with insulin resistance. In addition, NGI001 supplementation suppressed hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation but had little effect on kidney function. In-depth investigations showed that NGI001 ameliorated fat deposition and increased AMPK phosphorylation, resulting in phosphorylation of its major downstream target, acetyl-CoA carboxylase, in human hepatocyte HuS-E/2 cells. This cascade ultimately led to the down-regulation of downstream fatty acid synthesis-related molecules and the up-regulation of downstream β oxidation-associated molecules. Surprisingly, NGI001 decreased gene and protein expression of SGLT1 and SGLT2 and glucose uptake in oleic acid-treated HuS-E/2 cells.
Conclusion and implications: Our findings suggest the novel SGLT2 inhibitor, NGI001 has therapeutic potential to attenuate or delay the onset of diet-induced metabolic diseases and NAFLD.
© 2019 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander, S. P. H. , Roberts, R. E. , Broughton, B. R. S. , Sobey, C. G. , George, C. H. , Stanford, S. C. , … Ahluwalia, A. (2018). Goals and practicalities of immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry: A guide for submission to the British Journal of Pharmacology. British Journal of Pharmacology, 175, 407–411. 10.1111/bph.14112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

