Cognitive and social congruence in peer-assisted learning - A scoping review
- PMID: 31498826
- PMCID: PMC6733464
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222224
Cognitive and social congruence in peer-assisted learning - A scoping review
Abstract
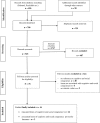
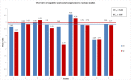
This scoping review presents an overview of cognitive and social congruence in peer assisted learning (PAL), as the positive effects of PAL have been shown to rely on these critical factors. The scoping review followed the guidelines of the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement. Databases were systematically searched for articles that focus on PAL and cognitive and social congruence. Participants of the studies included were medical, health science, polytechnic, law and paramedic students. Studies that assessed cognitive and social congruence by questionnaires with a 5-point Likert scale were regarded for meta-analytic pooling. Sixteen of 786 identified articles were included in the review, whereof 9 studies were considered for meta-analytic pooling. The meta-analytic pooling showed that tutees tend to see their student tutors as cognitively (Mweighted = 3.84; range of Mweighted = 2.69-4.56) and socially congruent (Mweighted = 3.95; range of Mweighted = 2.33-4.57). Further, characteristics of student tutors are summarized. This scoping review presents an overview and operationalization of cognitive and social congruence in PAL. Based on the presented meta-analytic pooling, cognitive and social congruence were found to represent relevant key factors in the PAL context. Thus, this theoretical background should be acknowledged as a core concept for tutorials within the medical curriculum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
'Student tutors go online' - Investigation of cognitive and social congruence in online student tutorials - a longitudinal study.Med Educ Online. 2022 Dec;27(1):2100038. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2022.2100038. Med Educ Online. 2022. PMID: 35815340 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative analysis of cognitive and social congruence in peer-assisted learning - The perspectives of medical students, student tutors and lecturers.Med Educ Online. 2020 Dec;25(1):1801306. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2020.1801306. Med Educ Online. 2020. PMID: 32744892 Free PMC article.
-
A novel instrument of cognitive and social congruence within peer-assisted learning in medical training: construction of a questionnaire by factor analyses.BMC Med Educ. 2020 Jul 8;20(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02129-x. BMC Med Educ. 2020. PMID: 32641115 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Peer-Assisted Learning in health professional education: a scoping review of systematic reviews.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):1467. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06434-7. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39695653 Free PMC article.
-
Peer-assisted learning (PAL) in undergraduate medical education: An overview.Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundhwes. 2017 Apr;121:74-81. doi: 10.1016/j.zefq.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundhwes. 2017. PMID: 28545616 Review.
Cited by
-
Confronting the Challenges of Anatomy Education in a Competency-Based Medical Curriculum During Normal and Unprecedented Times (COVID-19 Pandemic): Pedagogical Framework Development and Implementation.JMIR Med Educ. 2020 Oct 7;6(2):e21701. doi: 10.2196/21701. JMIR Med Educ. 2020. PMID: 32873536 Free PMC article.
-
A case-controlled trial evaluating the summative performance of the 3-D skills Model.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Sep 2;24(1):954. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05943-9. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39223576 Free PMC article.
-
A Preference for Peers over Faculty in the Pandemic Era: Development and Evaluation of a Medical Student-led Virtual Physiology Exam Review.Med Sci Educ. 2021 Dec 2;32(1):3-5. doi: 10.1007/s40670-021-01478-6. eCollection 2022 Feb. Med Sci Educ. 2021. PMID: 34877073 Free PMC article.
-
Tutors´ and Students' Agreement on Social and Cognitive Congruence in a Sonography Peer-assisted-learning Scenario.Med Sci Educ. 2023 Jun 9;33(4):903-911. doi: 10.1007/s40670-023-01814-y. eCollection 2023 Aug. Med Sci Educ. 2023. PMID: 37546194 Free PMC article.
-
Impacts of Learning Assistants on Student Belonging and Confidence Vary Across Science Disciplines and Course Contexts.CBE Life Sci Educ. 2025 Jun 1;24(2):ar26. doi: 10.1187/cbe.24-07-0179. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2025. PMID: 40215463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bene KL, Bergus G. When Learners Become Teachers: A Review of Peer Teaching in Medical Student Education. Fam Med. 2014;46(10):783–7. - PubMed
-
- Topping K, Ehly S. Introduction to peer-assisted learning. Peer-assisted learning. 1998;1:1–23.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources