Chemical Enhancement of Irreversible Electroporation: A Review and Future Suggestions
- PMID: 31500518
- PMCID: PMC6737874
- DOI: 10.1177/1533033819874128
Chemical Enhancement of Irreversible Electroporation: A Review and Future Suggestions
Abstract
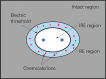
Irreversible electroporation has raised great interest in the past decade as a means of destroying cancers in a way that does not involve heat. Irreversible electroporation is a novel ablation technology that uses short high-voltage electrical pulses to enhance the permeability of tumor cell membranes and generate irreversible nano-sized structural defects or pores, thus leading to cell death. Irreversible electroporation has many advantages over thermal therapies due to its nonthermal mechanism: (1) reduced risk of injury to surrounding organs and (2) no "heat-sink" effect due to nearby blood vessels. However, so far, it has been difficult for irreversible electroporation to completely ablate large tumors (eg, >3 cm in diameter). In order to overcome this problem, many preclinical and clinical studies have been performed to improve the efficacy of IRE in the treatment of large size of tumors through a chemical perspective. Due to the distribution of electric field, irreversible electroporation region, reversible electroporation region, and intact region can be found in the treatment of irreversible electroporation. Thus, 2 types of chemical enhancements of irreversible electroporation were discussed in the article, such as the reversible electroporation region enhanced and the irreversible electroporation region enhanced. Specifically, the state-of-the-art results regarding the following approaches that have the potential to be used in the enhancement of irreversible electroporation were systematically reviewed in the article, including (1) combination with cytotoxic drugs, (2) calcium electroporation, (3) modification of cell membrane, and (4) modification of the tumor cell microenvironment. In the end, we concluded with 4 issues that should be addressed in the future for improving irreversible electroporation further in a chemical way.
Keywords: calcium electroporation; cell microenvironment; chemical enhancement; cytotoxic drugs; irreversible electroporation; surfactants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Study on Nonthermal Irreversible Electroporation of the Thyroid.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan 1;18:1533033819876307. doi: 10.1177/1533033819876307. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 31564220 Free PMC article.
-
Irreversible electroporation and electrochemotherapy in oncology: State of the art.Diagn Interv Imaging. 2022 Nov;103(11):499-509. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2022.09.009. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36266192 Review.
-
Irreversible electroporation for the ablation of liver tumors: are we there yet?Arch Surg. 2012 Nov;147(11):1053-61. doi: 10.1001/2013.jamasurg.100. Arch Surg. 2012. PMID: 23165618 Review.
-
Electrolytic Effects During Tissue Ablation by Electroporation.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Oct;15(5):NP95-NP103. doi: 10.1177/1533034615601549. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26323571
-
Irreversible Electroporation: An Emerging Immunomodulatory Therapy on Solid Tumors.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 7;12:811726. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.811726. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35069599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreatic Cancer-An Evolving Experimental and Clinical Method.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 23;24(5):4381. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054381. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Investigation for Large Volume, Focal Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption with High-Frequency Pulsed Electric Fields.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Dec 20;14(12):1333. doi: 10.3390/ph14121333. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34959733 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy of irreversible electroporation and cytokine-induced killer cells for treating mice bearing panc02 pancreatic-cancer xenografts.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023 Sep 19;35:101547. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2023.101547. eCollection 2023 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2023. PMID: 37745985 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemotherapy for head and neck cancers: possibilities and limitations.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 15;14:1353800. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1353800. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38434679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-frequency irreversible electroporation improves survival and immune cell infiltration in rodents with malignant gliomas.Front Oncol. 2023 May 5;13:1171278. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1171278. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37213298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paiella S, Butturini G, Frigerio I, et al. Safety and feasibility of irreversible electroporation (IRE) in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: results of a prospective study. Dig Surg. 2015;32(2):90–97. - PubMed
-
- Lencioni R, Cioni D, Della Pina C, Crocetti L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: new options for image-guided ablation. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010;17(4):399–403. - PubMed
-
- Zhang B, Moser MA, Zhang EM, Luo Y, Liu C, Zhang W. A review of radiofrequency ablation: large target tissue necrosis and mathematical modelling. Phys Med. 2016;32:961–971. - PubMed
-
- Vroomen LGPH, Petre EN, Cornelis FH, Solomon SB, Srimathveeravalli G. Irreversible electroporation and thermal ablation of tumors in the liver, lung, kidney and bone: what are the differences? Diagn Interv Imaging. 2017;98(9):609–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

