Impact of Intermittent Hypoxia on Sepsis Outcomes in a Murine Model
- PMID: 31501504
- PMCID: PMC6733849
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49381-w
Impact of Intermittent Hypoxia on Sepsis Outcomes in a Murine Model
Abstract
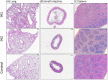
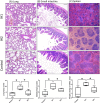
Sleep apnea has been associated with a variety of diseases, but its impact on sepsis outcome remains unclear. This study investigated the effect of intermittent hypoxia [IH]-the principal feature of sleep apnea-on murine sepsis. 5-week-old male C57BL6 mice were assigned to groups receiving severe IH (O2 fluctuating from room air to an O2 nadir of 5.7% with a cycle length of 90 seconds), mild IH (room air to 12%, 4 minutes/cycle), or room air for 3 weeks. Sepsis was induced by cecal ligation and puncture and survival was monitored. Sepsis severity was evaluated by murine sepsis scores, blood bacterial load, plasma tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α]/interleukin-6 [IL-6] levels and histopathology of vital organs. Compared with normoxic controls, mice subjected to severe IH had earlier mortality, a lower leukocyte count, higher blood bacterial load, higher plasma TNF-α and IL-6 levels, more severe inflammatory changes in the lung, spleen and small intestine. Mice subjected to mild IH did not differ from normoxic controls, except a higher IL-6 level after sepsis induced. The adverse impact of severe IH was reversed following a 10-day normoxic recovery. In conclusion, severe IH, not mild IH, contributed to poorer outcomes in a murine sepsis model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prolonged Exposures to Intermittent Hypoxia Promote Visceral White Adipose Tissue Inflammation in a Murine Model of Severe Sleep Apnea: Effect of Normoxic Recovery.Sleep. 2017 Mar 1;40(3). doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsw074. Sleep. 2017. PMID: 28329220
-
Time-dependent inflammatory factor production and NFκB activation in a rodent model of intermittent hypoxia.Swiss Med Wkly. 2011 Nov 30;141:w13309. doi: 10.4414/smw.2011.13309. eCollection 2011. Swiss Med Wkly. 2011. PMID: 22143914
-
Normoxic Recovery Mimicking Treatment of Sleep Apnea Does Not Reverse Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Bacterial Dysbiosis and Low-Grade Endotoxemia in Mice.Sleep. 2016 Oct 1;39(10):1891-1897. doi: 10.5665/sleep.6176. Sleep. 2016. PMID: 27397563 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent hypoxia promotes melanoma lung metastasis via oxidative stress and inflammation responses in a mouse model of obstructive sleep apnea.Respir Res. 2018 Feb 12;19(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0727-x. Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 29433520 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor-4 mediated inflammation is involved in the cardiometabolic alterations induced by intermittent hypoxia.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:620258. doi: 10.1155/2015/620258. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25873766 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Apnea, Intermittent Hypoxemia, and Bradycardia Events Predict Late-Onset Sepsis in Infants Born Extremely Preterm.J Pediatr. 2024 Aug;271:114042. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2024.114042. Epub 2024 Apr 2. J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38570031 Free PMC article.
-
A novel model of urosepsis in rats developed by injection of Escherichia coli into the renal pelvis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 5;13:1074488. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1074488. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36685507 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of amino acid metabolism‑related genes as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in sepsis through machine learning.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Dec 20;29(2):36. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12786. eCollection 2025 Feb. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39776890 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

