Evaluation of toxicity of Bilsaan stem bark extracts in Swiss Albino mice
- PMID: 31501650
- PMCID: PMC6728132
Evaluation of toxicity of Bilsaan stem bark extracts in Swiss Albino mice
Abstract
Objective: Sambucus nigra commonly known as Bilsaan is used extensively in traditional medicine in Saudi Arabia to treat various types of illness. The establishment of safe dose of S. nigra is crucial while considering health-promoting benefits as exposure to excess amount may cause undesirable effects. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the acute oral toxicity of ethanolic (Eth) and methanolic (Meth) extracts from the bark of Bilsaan (Bil) in mice.
Materials and methods: The acute oral toxicity study of Eth-Bil and Meth-Bil extracts was carried out by the administration of 10, 100, and 1000 mg/kg body weight to mice in the 1st phase. According to the observation of the 1st phase, the Eth-Bil extract was given 50, 100, 200, and 400 while Meth-Bil was administered 200, 400, 800, and 1600 mg/kg body weight.
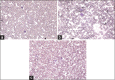
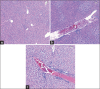
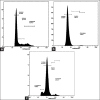
Results: The LD50 of the S. nigra (Bilsaan) methanol and ethanol extracts in mice was determined to be 31.62 mg/kg body weight for both of the extracts as calculated by Lorke's method. The gross observation of systemic organs demonstrated 10-90% increase in the weight of organs of animals treated with increasing concentration of extracts in comparison to control. Similarly, the hematological analyses also showed abnormality and reduction in total leukocytes count exposed with the higher concentration of extracts.
Conclusions: The results indicate that the oral administration of Eth-Bil and Meth-Bil extracts produce a significant toxic effect in mice but support in the establishment of safe dose range, as the intake of high doses of S. nigra (Bilsaan) extracts may exhibit mild organ toxicity.
Keywords: Acute toxicity; Bilsaan; Extracts.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Effect of Bilsaan, Sambucus nigra Stem Exudate, on the OVA-Induced Allergic Asthma in Mice.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jun 14;2020:3620192. doi: 10.1155/2020/3620192. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32617136 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and sub-acute toxicity of the methanolic extract of Pteleopsis hylodendron stem bark.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Sep 1;137(1):70-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.04.032. Epub 2011 May 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21645604
-
Toxicological studies of stem bark extract from Schefflera barteri Harms (Araliaceae).BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Mar 7;15:44. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0581-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 25887990 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and subacute toxicity profile of ethanolic stem bark extract of Albizia coriaria Welw. ex Oliv. in Wistar albino rats.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Jan 12;12:178-185. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.01.005. eCollection 2024 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38304700 Free PMC article.
-
Final report on the safety assessment of capsicum annuum extract, capsicum annuum fruit extract, capsicum annuum resin, capsicum annuum fruit powder, capsicum frutescens fruit, capsicum frutescens fruit extract, capsicum frutescens resin, and capsaicin.Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 1:3-106. doi: 10.1080/10915810601163939. Int J Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17365137 Review.
Cited by
-
Mycochemistry, antioxidant content, and antioxidant potentiality of the ethanolic extract of Pleurotus florida and its anti-cancerous effect on HeLa cancer cell line, and antitumor effect on HeLa-implanted mice.Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2023 Jan-Feb;17(1):18-35. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2023. PMID: 36704494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu RH. Potential synergy of phytochemicals in cancer prevention:Mechanism of action. J Nutr. 2004;134:3479S–85. - PubMed
-
- Block G, Patterson B, Subar A. Fruit, vegetables, and cancer prevention:A review of the epidemiological evidence. Nutr Cancer. 1992;18:1–29. - PubMed
-
- Liu JR, Dong HW, Chen BQ, Zhao P, Liu RH. Fresh apples suppress mammary carcinogenesis and proliferative activity and induce apoptosis in mammary tumors of the Sprague-Dawley rat. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:297–304. - PubMed
-
- Willett WC. Balancing life-style and genomics research for disease prevention. Science. 2002;296:695–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
