Interictal epileptiform discharges shape large-scale intercortical communication
- PMID: 31501850
- PMCID: PMC6821283
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awz269
Interictal epileptiform discharges shape large-scale intercortical communication
Abstract
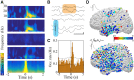
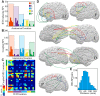
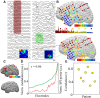
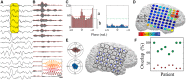
Dynamic interactions between remote but functionally specialized brain regions enable complex information processing. This intercortical communication is disrupted in the neural networks of patients with focal epilepsy, and epileptic activity can exert widespread effects within the brain. Using large-scale human intracranial electroencephalography recordings, we show that interictal epileptiform discharges (IEDs) are significantly coupled with spindles in discrete, individualized brain regions outside of the epileptic network. We found that a substantial proportion of these localized spindles travel across the cortical surface. Brain regions that participate in this IED-driven oscillatory coupling express spindles that have a broader spatial extent and higher tendency to propagate than spindles occurring in uncoupled regions. These altered spatiotemporal oscillatory properties identify areas that are shaped by epileptic activity independent of IED or seizure detection. Our findings suggest that IED-spindle coupling may be an important mechanism of interictal global network dysfunction that could be targeted to prevent disruption of normal neural activity.
Keywords: epilepsy; intercortical; interictal epileptiform discharge; oscillation; sleep spindle.
© The Author(s) (2019). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures

Comment in
-
Reply: Interactions of interictal epileptic discharges with sleep slow waves and spindles.Brain. 2020 Apr 1;143(4):e28. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa042. Brain. 2020. PMID: 32211754 No abstract available.
-
Interactions of interictal epileptic discharges with sleep slow waves and spindles.Brain. 2020 Apr 1;143(4):e27. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa041. Brain. 2020. PMID: 32275298 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Interaction of interictal epileptiform activity with sleep spindles is associated with cognitive deficits and adverse surgical outcome in pediatric focal epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2024 Jan;65(1):190-203. doi: 10.1111/epi.17810. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Epilepsia. 2024. PMID: 37983643 Free PMC article.
-
Interictal discharges spread along local recurrent networks between tubers and surrounding cortex.J Physiol. 2025 Apr;603(8):2425-2441. doi: 10.1113/JP288141. Epub 2025 Mar 17. J Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40096620 Free PMC article.
-
The seizure onset zone drives state-dependent epileptiform activity in susceptible brain regions.Clin Neurophysiol. 2019 Sep;130(9):1628-1641. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2019.05.032. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Clin Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31325676 Free PMC article.
-
Defining epileptogenic networks: Contribution of SEEG and signal analysis.Epilepsia. 2017 Jul;58(7):1131-1147. doi: 10.1111/epi.13791. Epub 2017 May 20. Epilepsia. 2017. PMID: 28543030 Review.
-
The role of interictal discharges in ictogenesis - A dynamical perspective.Epilepsy Behav. 2021 Aug;121(Pt B):106591. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.106591. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Epilepsy Behav. 2021. PMID: 31806490 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of epilepsy: electromagnetic stimulation-mediated neuromodulation therapy and new technologies.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Apr 1;20(4):917-935. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01444. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38989927 Free PMC article.
-
E-Suture: Mixed-Conducting Suture for Medical Devices.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Sep;13(24):e2302613. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202302613. Epub 2024 Jan 14. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38150402 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of epileptogenic networks via neuroplasticity in neural mass models.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Dec 3;20(12):e1012666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012666. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 39625956 Free PMC article.
-
Does epileptic activity impair sleep-related memory consolidation in epilepsy? A critical and systematic review.J Clin Sleep Med. 2022 Oct 1;18(10):2481-2495. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.10166. J Clin Sleep Med. 2022. PMID: 35866226 Free PMC article.
-
Closed-loop electrical stimulation prevents focal epilepsy progression and long-term memory impairment.Nat Neurosci. 2025 Aug;28(8):1753-1762. doi: 10.1038/s41593-025-01988-1. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Nat Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40551024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alarcon G, Garcia Seoane JJ, Binnie CD, Martin Miguel MC, Juler J, Polkey CE, et al.Origin and propagation of interictal discharges in the acute electrocorticogram. Implications for pathophysiology and surgical treatment of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 1997; 120 (Pt 12): 2259–82. - PubMed
-
- Bartolomei F, Lagarde S, Wendling F, McGonigal A, Jirsa V, Guye M, et al.Defining epileptogenic networks: Contribution of SEEG and signal analysis. Epilepsia 2017; 58: 1131–47. - PubMed
-
- Benchenane K, Peyrache A, Khamassi M, Tierney PL, Gioanni Y, Battaglia FP, et al.Coherent theta oscillations and reorganization of spike timing in the hippocampal- prefrontal network upon learning. Neuron 2010; 66: 921–36. - PubMed

