Recombinant production of a hard-to-express membrane-bound cytochrome P450 in different yeasts-Comparison of physiology and productivity
- PMID: 31502285
- PMCID: PMC7027447
- DOI: 10.1002/yea.3441
Recombinant production of a hard-to-express membrane-bound cytochrome P450 in different yeasts-Comparison of physiology and productivity
Abstract
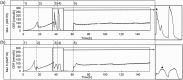
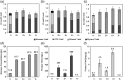
Cytochrome P450s comprise one of the largest protein superfamilies. They occur in every kingdom of life and catalyse a variety of essential reactions. Their production is of utmost interest regarding biotransformation and structure-function elucidation. However, they have proven hard to express due to their membrane anchor, their complex co-factor requirements and their need for a redox-partner. In our study, we investigated and compared different yeast strains for the production of the plant cytochrome P450 chalcone 3-hydroxylase. To our knowledge, this is the first study evaluating different yeasts for the expression of this abundant and highly significant protein superfamily. Saccharomyces cerevisiae and three different strains of Pichia pastoris expressing chalcone 3-hydroxylase were cultivated in controlled bioreactor runs and evaluated regarding physiological parameters and expression levels of the cytochrome P450. Production differed significantly between the different strains and was found highest in the investigated P. pastoris MutS strain KM71H where 8 mg P450 per gram dry cell weight were detected. We believe that this host could be suitable for the expression of many eukaryotic, especially plant-derived, cytochrome P450s as it combines high specific product yields together with straightforward cultivation techniques for achieving high biomass concentrations. Both factors greatly facilitate subsequent establishment of purification procedures for the cytochrome P450 and make the yeast strain an ideal platform for biotransformation as well.
Keywords: Pichia pastoris; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; chalcone 3-hydroxylase; physiology; recombinant protein production; yeast.
© 2019. The Authors. Yeast published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Over-expression of ICE2 stabilizes cytochrome P450 reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris.Biotechnol J. 2015 Apr;10(4):623-35. doi: 10.1002/biot.201400780. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Biotechnol J. 2015. PMID: 25641738
-
Recombinant production of eukaryotic cytochrome P450s in microbial cell factories.Biosci Rep. 2018 Mar 5;38(2):BSR20171290. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171290. Print 2018 Apr 27. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29436484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox Engineering by Ectopic Overexpression of NADH Kinase in Recombinant Pichia pastoris (Komagataella phaffii): Impact on Cell Physiology and Recombinant Production of Secreted Proteins.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Mar 2;86(6):e02038-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02038-19. Print 2020 Mar 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31757828 Free PMC article.
-
Improved NADPH Regeneration for Fungal Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase by Co-Expressing Bacterial Glucose Dehydrogenase in Resting-Cell Biotransformation of Recombinant Yeast.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Dec 28;26(12):2076-2086. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1605.05090. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27666994
-
Functional expression of eukaryotic cytochrome P450s in yeast.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2021 Mar;118(3):1050-1065. doi: 10.1002/bit.27630. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2021. PMID: 33205834 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional expression and regulation of eukaryotic cytochrome P450 enzymes in surrogate microbial cell factories.Eng Microbiol. 2022 Jan 19;2(1):100011. doi: 10.1016/j.engmic.2022.100011. eCollection 2022 Mar. Eng Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 39628612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current state and future perspectives of cytochrome P450 enzymes for C-H and C=C oxygenation.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022 May 8;7(3):887-899. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.04.009. eCollection 2022 Sep. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35601824 Free PMC article.
-
Chances and drawbacks of derepressed recombinant enzyme production in continuous cultivations with Komagataella phaffii.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 10;13:1523037. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1523037. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40129455 Free PMC article.
-
First purified recombinant CYP75B including transmembrane helix with unexpected high substrate specificity to (2R)-naringenin.Sci Rep. 2022 May 20;12(1):8548. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11556-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35595763 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous expression of a novel linoleic acid isomerase BBI, and effect of fusion tags on its performance.Curr Res Food Sci. 2022 Aug 30;5:2053-2060. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.07.013. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 36345432 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alugoju, P. , Janardhanshetty, S. S. , Subaramanian, S. , Periyasamy, L. , & Dyavaiah, M. (2018). Quercetin Protects Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae pep4 Mutant from Oxidative and Apoptotic Stress and Extends Chronological Lifespan. Current Microbiology, 75, 519–530. - PubMed
-
- Birch, R. M. , & Walker, G. M. (2000). Influence of magnesium ions on heat shock and ethanol stress responses of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 26, 678–687. - PubMed
-
- Byrne, B. (2015). Pichia pastoris as an expression host for membrane protein structural biology. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 32, 9–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
