GIT1 regulates angiogenic factor secretion in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via NF-κB/Notch signalling to promote angiogenesis
- PMID: 31502302
- PMCID: PMC6869488
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12689
GIT1 regulates angiogenic factor secretion in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via NF-κB/Notch signalling to promote angiogenesis
Abstract
Objectives: Osteogenesis is coupled with angiogenesis during bone remodelling. G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) kinase 2-interacting protein-1 (GIT1) is an important protein that participates in fracture healing by regulating angiogenesis. This study investigated whether GIT1 could affect bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) to secrete angiogenic factors to enhance fracture healing by promoting angiogenesis and its possible mechanism.
Materials and methods: The angiogenesis of mice post-fracture was detected by micro-CT and immunofluorescence. Subsequently, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) level in mouse and human BMSCs (hBMSCs) under TNF-α stimulation was detected. The hBMSCs were transfected with GIT1 shRNAs to further explore the relationship between GIT1 and VEGF and angiogenesis in vitro. Furthermore, based on previous research on GIT1, possible signal pathways were investigated.
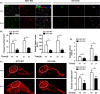
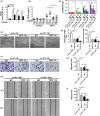
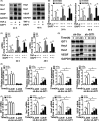
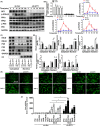
Results: GIT1 knockout mice exhibited impaired angiogenesis and delayed fracture healing. And GIT1 deficiency remarkably reduced the expression of VEGF mRNA in BMSCs, which affected the proliferation and migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. GIT1 knockdown inhibited the activation of Notch and NF-κB signals by decreasing nuclear transportation of NICD and P65/P50, respectively. Overexpression of the canonical NF-κB subunits P65 and P50 markedly increased NICD-dependent activation of recombination signal-binding protein-jκ reporter. Finally, GIT1 enhanced the affinity of NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO) for K63-linked ubiquitin chains via interaction with NEMO coiled-coil 2 domains.
Conclusion: These data revealed a positive role for GIT1 by modulating the Notch/NF-κB signals which promoting paracrine of BMSCs to enhance angiogenesis and fracture healing.
Keywords: GIT1; NF-κB; Notch; angiogenesis; fracture healing.
© 2019 The Authors. Cell Proliferation Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have a conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
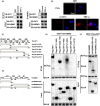
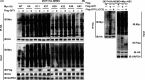
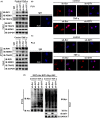
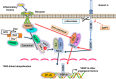
References
-
- Tsiridis E, Upadhyay N, Giannoudis P. Molecular aspects of fracture healing: which are the important molecules? Injury. 2007;38(Suppl 1):S11‐25. - PubMed
-
- Kon T, Cho TJ, Aizawa T, et al. Expression of osteoprotegerin, receptor activator of NF‐kappaB ligand (osteoprotegerin ligand) and related proinflammatory cytokines during fracture healing. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16(6):1004‐1014. - PubMed
-
- Bielby R, Jones E, McGonagle D. The role of mesenchymal stem cells in maintenance and repair of bone. Injury. 2007;38(Suppl 1):S26‐32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81772351/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81520108018/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81472080/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81772352/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 814/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BE2017755/Jiangsu Committee of Science and Technology-Social Development Plan
- WSN-011/Jiangsu Six Talents Peak
- 201505005/Nanjing Committee of Science and Technology
- YKK17060/Medical Science and technology development Foundation from Nanjing Department of Health
- KYLX16_1105/Research Innovation Program for Academic Degree College Graduates of Jiangsu
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

