CE-MS with electrokinetic supercharging and application to determination of neurotransmitters
- PMID: 31502303
- PMCID: PMC6947659
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.201900203
CE-MS with electrokinetic supercharging and application to determination of neurotransmitters
Abstract
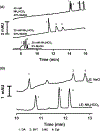
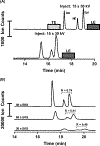
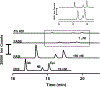
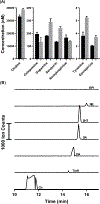
Electrokinetic supercharging (EKS) is known as one of the most effective online electrophoretic preconcentration techniques, though pairing with it with mass spectrometry has presented challenges. Here, EKS is successfully paired with ESI-MS/MS to provide a sensitive and robust method for analysis of biogenic amines in biological samples. Injection parameters including electric field strength and the buffer compositions used for the separation and focusing were investigated to achieve suitable resolution, high sensitivity, and compatibility with ESI-MS. Using EKS, the sensitivity of the method was improved 5000-fold compared to a conventional hydrodynamic injection with CZE. The separation allowed for baseline resolution of several neurotransmitters within 16 min with LODs down to 10 pM. This method was applied to targeted analysis of seven biogenic amines from rat brain stem and whole Drosophila tissue. This is the first method to use EKS with CE-ESI-MS/MS to analyze biological samples.
Keywords: Biological samples; CE; CE-MS; Electrokinetic supercharging; Neurotransmitters.
© 2019 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
References
-
- Chen G, Ewing AG Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1997, 11, 59. - PubMed
-
- Lapainis T, Sweedler JV, J Chromatogr A 2008, 1184, 144–158. - PubMed
-
- Monton MRN, Soga T, Chromatogr J. A 2007, 1168, 237–246. - PubMed
-
- Faserl K, Sarg B, Sola L, Lindner HH, Proteomics 2017, 17, 1–5. - PubMed
-
- Mateos-Vivas M, Domínguez-Álvarez J, Rodríguez-Gonzalo E, Carabias-Martínez R, Food Chem. 2017, 233, 38–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

