Chloroquine differentially modulates coronary vasodilation in control and diabetic mice
- PMID: 31503328
- PMCID: PMC6989957
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14864
Chloroquine differentially modulates coronary vasodilation in control and diabetic mice
Abstract
Background and purpose: Chloroquine is a traditional medicine to treat malaria. There is increasing evidence that chloroquine not only induces phagocytosis but regulates vascular tone. Few reports investigating the effect of chloroquine on vascular responsiveness of coronary arteries have been made. In this study, we examined how chloroquine affected endothelium-dependent relaxation in coronary arteries under normal and diabetic conditions.
Experimental approach: We isolated coronary arteries from mice and examined endothelium-dependent relaxation (EDR). Human coronary endothelial cells and mouse coronary endothelial cells isolated from control and diabetic mouse (TALLYHO/Jng [TH] mice, a spontaneous type 2 diabetic mouse model) were used for the molecular biological or cytosolic NO and Ca2+ measurements.
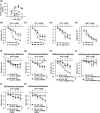
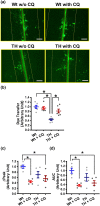
Key results: Chloroquine inhibited endothelium-derived NO-dependent relaxation but had negligible effect on endothelium-derived hyperpolarization (EDH)-dependent relaxation in coronary arteries of control mice. Chloroquine significantly decreased NO production in control human coronary endothelial cells partly by phosphorylating eNOSThr495 (an inhibitory phosphorylation site of eNOS) and attenuating the rise of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration after stimulation. EDR was significantly inhibited in diabetic mice in comparison to control mice. Interestingly, chloroquine enhanced EDR in diabetic coronary arteries by, specifically, increasing EDH-dependent relaxation due partly to its augmenting effect on gap junction activity in diabetic mouse coronary endothelial cells.
Conclusions and implications: These data indicate that chloroquine affects vascular relaxation differently under normal and diabetic conditions. Therefore, the patients' health condition such as coronary macrovascular or microvascular disease, with or without diabetes, must be taken account into the consideration when selecting chloroquine for the treatment of malaria.
© 2019 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vascular hypoxic preconditioning relies on TRPV4-dependent calcium influx and proper intercellular gap junctions communication.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Sep;32(9):2241-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.252783. Epub 2012 Jul 19. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22814746
-
Restoration of impaired endothelium-dependent coronary vasodilation in failing heart: role of eNOS phosphorylation and CGMP/cGK-I signaling.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):H2782-90. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00831.2006. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17322419
-
Important Roles of Endothelium-Dependent Hyperpolarization in Coronary Microcirculation and Cardiac Diastolic Function in Mice.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020 Jan;75(1):31-40. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000763. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31895878
-
Endothelium-Dependent Hyperpolarization (EDH) in Diabetes: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 31;20(15):3737. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153737. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31370156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitric oxide and coronary vascular endothelium adaptations in hypertension.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009;5:1075-87. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s7464. Epub 2009 Dec 29. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009. PMID: 20057900 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Modulation as a Therapeutic Option During the SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak: The Case for Antimalarial Aminoquinolines.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 28;11:2159. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02159. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32983179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Hypoxia Decreases Endothelial Connexin 40, Attenuates Endothelium-Dependent Hyperpolarization-Mediated Relaxation in Small Distal Pulmonary Arteries, and Leads to Pulmonary Hypertension.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Dec 15;9(24):e018327. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.018327. Epub 2020 Dec 12. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 33307937 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxychloroquine induces endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent relaxation of rat aorta.Turk J Med Sci. 2022 Jun;52(3):848-857. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5382. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Turk J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36326331 Free PMC article.
-
Sex based cardiovascular differences in adult and middle-aged hypertensive schlager mice.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 28;15(1):31679. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16459-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40877340 Free PMC article.
-
Bitter taste receptor agonists induce vasorelaxation in porcine coronary arteries.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 7;16:1578913. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1578913. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40693268 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

