The LUFS domain, its transcriptional regulator proteins, and drug resistance in the fungal pathogen Candida auris
- PMID: 31503375
- PMCID: PMC6798126
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3727
The LUFS domain, its transcriptional regulator proteins, and drug resistance in the fungal pathogen Candida auris
Abstract
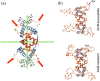
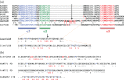
The LUFS domain (LUG/LUH, Flo8, single-strand DNA-binding protein [SSBP]) is a well-conserved and apparently ancient region found in diverse proteins and taxa. This domain, which has as its most obvious structural feature a series of three helices, has been identified in transcriptional regulator proteins of animals, plants, and fungi. Recently, in these pages (Wang et al., Protein Sci., 2019, 28:788-793), the first crystal structure of a LUFS domain was reported, for the human SSBP2, a transcriptional repressor. We briefly address how the new insights into LUFS structures might contribute to a better understanding of an important transcriptional activator of yeasts that contains the LUFS domain, Flo8, and consider how a focus on the LUFS domain and its variation could help us to understand etiologies of drug resistance in a recently emerged pathogenic fungus, Candida auris.
Keywords: Candida; LUFS domain; activation and repression domains; amphotericin B; antifungal resistance mechanisms; filamentation in fungi; flocculence; single nucleotide polymorphisms; transcription factors; whole-genome sequence comparisons.
© 2019 The Protein Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of the LUFS domain of human single-stranded DNA binding Protein 2 (SSBP2).Protein Sci. 2019 Apr;28(4):788-793. doi: 10.1002/pro.3581. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Protein Sci. 2019. PMID: 30676665 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Analysis of Candida auris Implicates Hsp90 in Morphogenesis and Azole Tolerance and Cdr1 in Azole Resistance.mBio. 2019 Jan 29;10(1):e02529-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02529-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30696744 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular and genetic basis of antifungal resistance in the emerging fungal pathogen Candida auris.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2022 Dec;70:102208. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2022.102208. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36242897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous Emergence of Multidrug-Resistant Candida auris on 3 Continents Confirmed by Whole-Genome Sequencing and Epidemiological Analyses.Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Jan 15;64(2):134-140. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw691. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Clin Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 27988485 Free PMC article.
-
Candida and candidaemia. Susceptibility and epidemiology.Dan Med J. 2013 Nov;60(11):B4698. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 24192246 Review.
Cited by
-
Acquired Triazole Resistance Alters Pathogenicity-Associated Features in Candida auris in an Isolate-Dependent Manner.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;9(12):1148. doi: 10.3390/jof9121148. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132749 Free PMC article.
-
Candida auris: a global pathogen that has taken root in Colombia.Biomedica. 2023 Aug 31;43(Sp. 1):278-287. doi: 10.7705/biomedica.7082. Biomedica. 2023. PMID: 37721898 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal Resistance in Candida auris: Molecular Determinants.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Sep 2;9(9):568. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9090568. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32887362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of Experimentally Evolved Candida auris Reveals Multiple Novel Mechanisms of Multidrug Resistance.mBio. 2021 Apr 5;12(2):e03333-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03333-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33820824 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Genome Sequences of the Emerging Fungal Pathogen Candida auris.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 27;11:560332. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.560332. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33193142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim TS, Ahn JY, Yoon JH, Kang HS. STA10 repression of STA gene expression is caused by a defective activator, flo8, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Curr Genet. 2003;44:261–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

