miR-106b-5p promotes aggressive progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting RUNX3
- PMID: 31503422
- PMCID: PMC6825988
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2511
miR-106b-5p promotes aggressive progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting RUNX3
Abstract
Background and objectives: The roles of microRNA(miR)-106b-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain unclear. We aimed here to investigate the clinical significance of miR-106b-5p expression in HCC and its underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Expression levels of miR-106b-5p in 108 HCC clinical samples by quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR. Associations of miR-106b-5p expression with various clinicopathological features and patients' prognosis were evaluated by Chi-square test, Kaplan-Meier, and Cox proportional regression analyses, respectively. The target gene of miR-106b-5p and their functions in HCC cells were investigated by luciferase reporter, CCK-8, and Transwell Matrigel invasion assays.
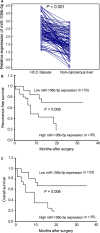
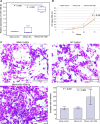
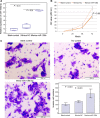
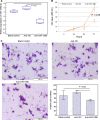
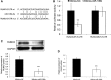
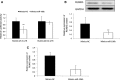
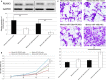
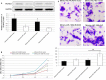
Results: miR-106b-5p expression was markedly higher in HCC tissues than in noncancerous adjacent liver tissues (P < .001). miR-106b-5p upregulation was significantly associated with advanced TNM stage (P = .02), short recurrence-free (P = .005), and overall (P = .001) survivals. Importantly, miR-106b-5p expression was an independent predictor of poor prognosis (P < .05). RUNX3 was identified as a direct target gene of miR-106b-5p in HCC cells. Functionally, miR-106b-5p upregulation promoted the viability and invasion of HCC cells, while enforced RUNX3 expression reversed the oncogenic effects of miR-106b-5p overexpression.
Conclusions: miR-106b-5p may serve as a potent prognostic marker for tumor recurrence and survival of HCC patients. miR-106b-5p may exert an oncogenic role in HCC via regulating its target gene RUNX3.
Keywords: cell viability; hepatocellular carcinoma; invasion; microRNA-106b-5p; overall survival; recurrence-free survival.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of miR-1266-5p serves as a prognostic biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma and facilitates tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion.Acta Biochim Pol. 2021 May 19;68(2):293-300. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_5569. Acta Biochim Pol. 2021. PMID: 34006084
-
MiR-877-5p suppresses cell growth, migration and invasion by targeting cyclin dependent kinase 14 and predicts prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 May;22(10):3038-3046. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201805_15061. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29863248
-
MicroRNA-424-5p acts as a potential biomarker and inhibits proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting TRIM29.Life Sci. 2019 May 1;224:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.028. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30876939
-
Relationship between RUNX3 methylation and hepatocellular carcinoma in Asian populations: a systematic review.Genet Mol Res. 2014 Jul 7;13(3):5182-9. doi: 10.4238/2014.July.7.11. Genet Mol Res. 2014. PMID: 25061743
-
miR-106b-25/miR-17-92 clusters: polycistrons with oncogenic roles in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 May 28;20(20):5962-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.5962. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24876719 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNA circSLC8A1 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells through targeting the miR-106b-5p /FOXJ3 axis.Cell Cycle. 2021 Dec;20(24):2597-2606. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1995968. Epub 2021 Nov 1. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34724864 Free PMC article.
-
Independent prognostic significance of tissue and circulating microrna biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 8;16(1):281. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02043-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40056315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR‑106b‑5p targeting SIX1 inhibits TGF‑β1‑induced pulmonary fibrosis and epithelial‑mesenchymal transition in asthma through regulation of E2F1.Int J Mol Med. 2021 Mar;47(3):04855. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4857. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Int J Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33495833 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-106b-5p inhibits growth and progression of lung adenocarcinoma cells by downregulating IGSF10.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jul 29;13(14):18740-18756. doi: 10.18632/aging.203318. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34351868 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNA Master Regulators in Breast Cancer.Cells. 2020 Jul 3;9(7):1610. doi: 10.3390/cells9071610. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32635183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet‐Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87‐108. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Di Bisceglie AM, Bruix J, et al. Design and endpoints of clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:698‐711. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245‐1255. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281‐297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

