CAC1 knockdown reverses drug resistance through the downregulation of P-gp and MRP-1 expression in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 31504073
- PMCID: PMC6736305
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222035
CAC1 knockdown reverses drug resistance through the downregulation of P-gp and MRP-1 expression in colorectal cancer
Abstract
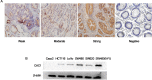
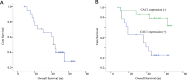
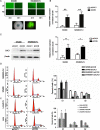
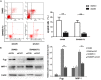
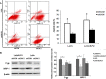
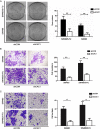
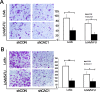
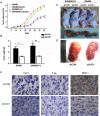
CDK2-associated cullin domain 1 (CAC1) is as a novel cell cycle regulator widely expressed in colorectal cancer (CRC). However, its expression and function in drug resistant CRC cells remains elusive. Therefore, the present study aimed to assess the biochemical function and relevance of CAC1 in drug resistant CRC cells, and detect the potential mechanism. For this purpose, a total of 83 CRC cases were collected for the immunohistochemical analysis of CAC1 expression. Functional studies (stable transfection, flow cytometry, colony formation, and invasion and migration assays) were performed in SW480, LoVo and their corresponding 5-FU resistant cells. In addition, a nude mice xenograft model was established for further observation in vivo. In the present study, CAC1 protein expression was higher in CRC tissues than that in normal tissues (P<0.05). Furthermore, CAC1 protein expression was higher in SW480/5-FU cells than in SW480 cells. CAC1 knockdown arrested 5-FU resistant cells at the G1/S phase and increased the sensitivity of 5-FU resistant cells to 5-FU by inducing apoptosis. In addition, CAC1 reduced the invasive and migration ability of SW480/5-FU and LoVo/5-FU cells in vitro, and reduced their tumorigenicity and metastatic ability in vivo. Finally, CAC1 knockdown resulted in decreased P-glycoprotein and MRP-1 protein expression. Based on these results, it can be concluded that CAC1 plays an important role in the occurrence and promotion of drug resistance in CRC. Therefore, the knockdown of CAC1 may be considered as a new strategy for the development of CRC drug resistance treatments in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Syndecan-2, negatively regulated by miR-20b-5p, contributes to 5-fluorouracil resistance of colorectal cancer cells via the JNK/ERK signaling pathway.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Nov 10;53(11):1547-1557. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmab124. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 34596215
-
The deoxycholic acid targets miRNA-dependent CAC1 gene expression in multidrug resistance of human colorectal cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Dec;44(12):2321-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.08.006. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22903020
-
Circ_0007031 enhances tumor progression and promotes 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer through regulating miR-133b/ABCC5 axis.Cancer Biomark. 2020;29(4):531-542. doi: 10.3233/CBM-200023. Cancer Biomark. 2020. PMID: 32865180
-
AHNAK2 confers 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer via activation of the AKT/GSK-3β signaling axis.Clin Exp Med. 2025 May 18;25(1):168. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01682-3. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40382757 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of drug resistance in nutrient-depleted colorectal cancer cells: insights into lysosomal and mitochondrial drug sequestration.Biol Open. 2024 Jul 15;13(10):bio060448. doi: 10.1242/bio.060448. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 39445740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel strategies to reverse chemoresistance in colorectal cancer.Cancer Med. 2023 May;12(10):11073-11096. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5594. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36645225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA ZFR promotes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells via the miR-147a/CACUL1 axis.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Aug;13(4):1793-1804. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-672. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36092343 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic silencing of miR-125a-3p promotes the progress of human cholangiocarcinoma via increasing CAC1 expression.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 15;10(12):e32528. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32528. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38994075 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Ovarian Cancer and Associated Gene Targets.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 18;14(24):6246. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246246. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Updates on Mechanisms of Resistance to 5-Fluorouracil and Reversal Strategies in Colon Cancer Treatment.Biology (Basel). 2021 Aug 31;10(9):854. doi: 10.3390/biology10090854. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34571731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

