Protein functional annotation of simultaneously improved stability, accuracy and false discovery rate achieved by a sequence-based deep learning
- PMID: 31504150
- PMCID: PMC7412958
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbz081
Protein functional annotation of simultaneously improved stability, accuracy and false discovery rate achieved by a sequence-based deep learning
Abstract
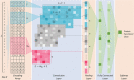
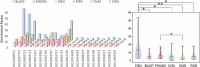
Functional annotation of protein sequence with high accuracy has become one of the most important issues in modern biomedical studies, and computational approaches of significantly accelerated analysis process and enhanced accuracy are greatly desired. Although a variety of methods have been developed to elevate protein annotation accuracy, their ability in controlling false annotation rates remains either limited or not systematically evaluated. In this study, a protein encoding strategy, together with a deep learning algorithm, was proposed to control the false discovery rate in protein function annotation, and its performances were systematically compared with that of the traditional similarity-based and de novo approaches. Based on a comprehensive assessment from multiple perspectives, the proposed strategy and algorithm were found to perform better in both prediction stability and annotation accuracy compared with other de novo methods. Moreover, an in-depth assessment revealed that it possessed an improved capacity of controlling the false discovery rate compared with traditional methods. All in all, this study not only provided a comprehensive analysis on the performances of the newly proposed strategy but also provided a tool for the researcher in the fields of protein function annotation.
Keywords: annotation accuracy; deep learning; false discovery rate; prediction stability; protein function prediction.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessing the Performances of Protein Function Prediction Algorithms from the Perspectives of Identification Accuracy and False Discovery Rate.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 8;19(1):183. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010183. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29316706 Free PMC article.
-
Convolutional neural network-based annotation of bacterial type IV secretion system effectors with enhanced accuracy and reduced false discovery.Brief Bioinform. 2020 Sep 25;21(5):1825-1836. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz120. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 31860715
-
PFmulDL: a novel strategy enabling multi-class and multi-label protein function annotation by integrating diverse deep learning methods.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Jun;145:105465. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105465. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35366467
-
Current directions in combining simulation-based macromolecular modeling approaches with deep learning.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2021 Sep;16(9):1025-1044. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2021.1918097. Epub 2021 May 31. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 33993816 Review.
-
The power of deep learning to ligand-based novel drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2020 Jul;15(7):755-764. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2020.1745183. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2020. PMID: 32228116 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Predicting Protein S-Nitrosylation Sites.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Feb 9;2021:5542224. doi: 10.1155/2021/5542224. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33628788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated COVID-19 Predictor: Differential expression analysis to reveal potential biomarkers and prediction of coronavirus using RNA-Seq profile data.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Aug;147:105684. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105684. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35687925 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Variation Prediction: A Summary From Different Views.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 25;9:795883. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.795883. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34901036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-RNA interactions between SARS-CoV-2 and host benefit viral development and evolution during COVID-19 infection.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Jan 17;23(1):bbab397. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab397. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 34585235 Free PMC article.
-
Improving protein domain classification for third-generation sequencing reads using deep learning.BMC Genomics. 2021 Apr 9;22(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07468-7. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33836667 Free PMC article.

