Clonal haematopoiesis in patients with degenerative aortic valve stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation
- PMID: 31504400
- PMCID: PMC7033916
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz591
Clonal haematopoiesis in patients with degenerative aortic valve stenosis undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation
Abstract
Aims: Clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP), defined as the presence of an expanded somatic blood cell clone without other haematological abnormalities, was recently shown to increase with age and is associated with coronary artery disease and calcification. The most commonly mutated CHIP genes, DNMT3A and TET2, were shown to regulate inflammatory potential of circulating leucocytes. The incidence of degenerative calcified aortic valve (AV) stenosis increases with age and correlates with chronic inflammation. We assessed the incidence of CHIP and its association with inflammatory blood cell phenotypes in patients with AV stenosis undergoing transfemoral aortic valve implantation (TAVI).
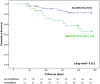
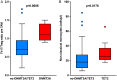
Methods and results: Targeted amplicon sequencing for DNMT3A and TET2 was performed in 279 patients with severe AV stenosis undergoing TAVI. Somatic DNMT3A- or TET2-CHIP-driver mutations with a VAF ≥ 2% were detected in 93 out of 279 patients (33.3%), with an age-dependent increase in the incidence from 25% (55-69 years) to 52.9% (90-100 years). Patients with DNMT3A- or TET2-CHIP-driver mutations did not differ from patients without such mutations in clinical parameters, concomitant atherosclerotic disease, blood cell counts, inflammatory markers, or procedural characteristics. However, patients with DNMT3A- or TET2-CHIP-driver mutations had a profoundly increased medium-term all-cause mortality following successful TAVI. Differential myeloid and T-cell distributions revealed pro-inflammatory T-cell polarization in DNMT3A-mutation carriers and increased pro-inflammatory non-classical monocytes in TET2-mutation carriers.
Conclusion: This is the first study to show that acquired somatic mutations in the most commonly mutated CHIP-driver genes occur frequently in patients with severe degenerative AV stenosis, are associated with increased pro-inflammatory leucocyte subsets, and confer a profound increase in mortality following successful TAVI.
Keywords: Aortic valve disease; Clonal haematopoiesis; Inflammation; TAVI.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Clonal haematopoiesis, aortic stenosis and reduced survival after TAVI.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019 Nov;16(11):650. doi: 10.1038/s41569-019-0275-1. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31527745 No abstract available.
-
A new opening on aortic stenosis: predicting prognosis with clonal haematopoiesis.Eur Heart J. 2020 Feb 21;41(8):940-942. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz752. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 31634387 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jaiswal S, Fontanillas P, Flannick J, Manning A, Grauman PV, Mar BG, Lindsley RC, Mermel CH, Burtt N, Chavez A, Higgins JM, Moltchanov V, Kuo FC, Kluk MJ, Henderson B, Kinnunen L, Koistinen HA, Ladenvall C, Getz G, Correa A, Banahan BF, Gabriel S, Kathiresan S, Stringham HM, McCarthy MI, Boehnke M, Tuomilehto J, Haiman C, Groop L, Atzmon G, Wilson JG, Neuberg D, Altshuler D, Ebert BL.. Age-related clonal hematopoiesis associated with adverse outcomes. N Engl J Med 2014;371:2488–2498. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jaiswal S, Natarajan P, Silver AJ, Gibson CJ, Bick AG, Shvartz E, McConkey M, Gupta N, Gabriel S, Ardissino D, Baber U, Mehran R, Fuster V, Danesh J, Frossard P, Saleheen D, Melander O, Sukhova GK, Neuberg D, Libby P, Kathiresan S, Ebert BL.. Clonal hematopoiesis and risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 2017;377:111–121. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fuster JJ, MacLauchlan S, Zuriaga MA, Polackal MN, Ostriker AC, Chakraborty R, Wu C-L, Sano S, Muralidharan S, Rius C, Vuong J, Jacob S, Muralidhar V, Robertson AAB, Cooper MA, Andrés V, Hirschi KK, Martin KA, Walsh K.. Clonal hematopoiesis associated with TET2 deficiency accelerates atherosclerosis development in mice. Science 2017;355:842–847. - PMC - PubMed

