Prognostic models will be victims of their own success, unless…
- PMID: 31504588
- PMCID: PMC6857506
- DOI: 10.1093/jamia/ocz145
Prognostic models will be victims of their own success, unless…
Abstract
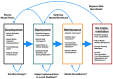
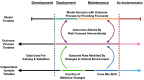
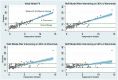
Predictive analytics have begun to change the workflows of healthcare by giving insight into our future health. Deploying prognostic models into clinical workflows should change behavior and motivate interventions that affect outcomes. As users respond to model predictions, downstream characteristics of the data, including the distribution of the outcome, may change. The ever-changing nature of healthcare necessitates maintenance of prognostic models to ensure their longevity. The more effective a model and intervention(s) are at improving outcomes, the faster a model will appear to degrade. Improving outcomes can disrupt the association between the model's predictors and the outcome. Model refitting may not always be the most effective response to these challenges. These problems will need to be mitigated by systematically incorporating interventions into prognostic models and by maintaining robust performance surveillance of models in clinical use. Holistically modeling the outcome and intervention(s) can lead to resilience to future compromises in performance.
Keywords: learning health system; model updating; predictive modeling.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Explicit causal reasoning is needed to prevent prognostic models being victims of their own success.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019 Dec 1;26(12):1675-1676. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocz197. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31722385 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Stead WW. Clinical implications and challenges of artificial intelligence and deep learning. JAMA 2018; 32011: 1107–8. doi:10.1037/h0030806. - PubMed
-
- Moons KGM, Altman DG, Vergouwe Y, Royston P.. Prognosis and prognostic research: application and impact of prognostic models in clinical practice. BMJ 2009; 3382: b606.. - PubMed
-
- Horvitz EF. Data to predictions and decisions: enabling evidence-based healthcare. 2010. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Evid... Accessed February 19, 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials