Tumor cells educate mesenchymal stromal cells to release chemoprotective and immunomodulatory factors
- PMID: 31504643
- PMCID: PMC7181721
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz090
Tumor cells educate mesenchymal stromal cells to release chemoprotective and immunomodulatory factors
Abstract
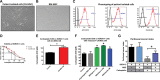
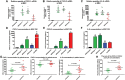
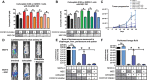
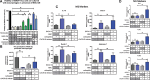
Factors released by surrounding cells such as cancer-associated mesenchymal stromal cells (CA-MSCs) are involved in tumor progression and chemoresistance. In this study, we characterize the mechanisms by which naïve mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) can acquire a CA-MSCs phenotype. Ovarian tumor cells trigger the transformation of MSCs to CA-MSCs by expressing pro-tumoral genes implicated in the chemoresistance of cancer cells, resulting in the secretion of high levels of CXC chemokine receptors 1 and 2 (CXCR1/2) ligands such as chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1), CXCL2, and interleukin 8 (IL-8). CXCR1/2 ligands can also inhibit the immune response against ovarian tumor cells. Indeed, through their released factors, CA-MSCs promote the differentiation of monocytes towards M2 macrophages, which favors tumor progression. When CXCR1/2 receptors are inhibited, these CA-MSC-activated macrophages lose their M2 properties and acquire an anti-tumoral phenotype. Both ex vivo and in vivo, we used a CXCR1/2 inhibitor to sensitize ovarian tumor cells to carboplatin and circumvent the pro-tumoral effects of CA-MSCs. Since high concentrations of CXCR1/2 ligands in patients' blood are associated with chemoresistance, CXCR1/2 inhibition could be a potential therapeutic strategy to revert carboplatin resistance.
Keywords: chemokines; chemoresistance; macrophages; mesenchymal stromal cells; ovarian adenocarcinoma.
© The Author(s) (2019). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, IBCB, SIBS, CAS.
Figures




References
-
- Beyar-Katz O., Magidey K., Ben-Tsedek N., et al. (2016). Bortezomib-induced pro-inflammatory macrophages as a potential factor limiting anti-tumour efficacy: Bortezomib-induced MM aggressiveness. J. Pathol. 239, 262–273. - PubMed
-
- Browne A., Sriraksa R., Guney T., et al. (2013). Differential expression of IL-8 and IL-8 receptors in benign, borderline and malignant ovarian epithelial tumours. Cytokine 64, 413–421. - PubMed
-
- Castells M., Thibault B., Mery E., et al. (2012). Ovarian ascites-derived Hospicells promote angiogenesis via activation of macrophages. Cancer Lett. 326, 59–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

