Insights into telomeric G-quadruplex DNA recognition by HMGB1 protein
- PMID: 31504744
- PMCID: PMC6765150
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz727
Insights into telomeric G-quadruplex DNA recognition by HMGB1 protein
Abstract
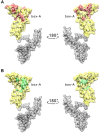
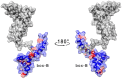
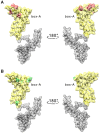
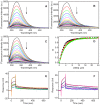
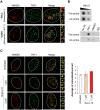
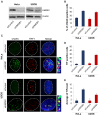
HMGB1 is a ubiquitous non-histone protein, which biological effects depend on its expression and subcellular location. Inside the nucleus, HMGB1 is engaged in many DNA events such as DNA repair, transcription and telomere maintenance. HMGB1 has been reported to bind preferentially to bent DNA as well as to noncanonical DNA structures like 4-way junctions and, more recently, to G-quadruplexes. These are four-stranded conformations of nucleic acids involved in important cellular processes, including telomere maintenance. In this frame, G-quadruplex recognition by specific proteins represents a key event to modulate physiological or pathological pathways. Herein, to get insights into the telomeric G-quadruplex DNA recognition by HMGB1, we performed detailed biophysical studies complemented with biological analyses. The obtained results provided information about the molecular determinants for the interaction and showed that the structural variability of human telomeric G-quadruplex DNA may have significant implications in HMGB1 recognition. The biological data identified HMGB1 as a telomere-associated protein in both telomerase-positive and -negative tumor cells and showed that HMGB1 gene silencing in such cells induces telomere DNA damage foci. Altogether, these findings provide a deeper understanding of telomeric G-quadruplex recognition by HMGB1 and suggest that this protein could actually represent a new target for cancer therapy.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human Telomeric G-Quadruplex Structures and G-Quadruplex-Interactive Compounds.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1587:171-196. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6892-3_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28324509 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of Telomere G-Quadruplexes Interferes with Human Herpesvirus 6A Chromosomal Integration.J Virol. 2017 Jun 26;91(14):e00402-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00402-17. Print 2017 Jul 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28468887 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Hybrid-2 type intramolecular human telomeric G-quadruplex in K+ solution: insights into structure polymorphism of the human telomeric sequence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(15):4927-40. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm522. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17626043 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Recognition of the Hybrid-Type G-Quadruplexes in Human Telomeres.Molecules. 2019 Apr 22;24(8):1578. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081578. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31013622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphism of human telomeric quadruplex structures.Biochimie. 2008 Aug;90(8):1172-83. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2008.02.026. Epub 2008 Mar 8. Biochimie. 2008. PMID: 18373984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmodium berghei HMGB1 controls the host immune responses and splenic clearance by regulating the expression of pir genes.J Biol Chem. 2024 Nov;300(11):107829. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107829. Epub 2024 Sep 27. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39341498 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1 is a Potential and Challenging Therapeutic Target for Parkinson's Disease.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jan;43(1):47-58. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01170-8. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 34797463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasmodium falciparum GBP2 Is a Telomere-Associated Protein That Binds to G-Quadruplex DNA and RNA.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 22;12:782537. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.782537. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35273922 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation by Protein Kinase C Weakens DNA-Binding Affinity and Folding Stability of the HMGB1 Protein.Biochemistry. 2024 Jul 16;63(14):1718-1722. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00194. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38916994 Free PMC article.
-
G-Quadruplex Binders Induce Immunogenic Cell Death Markers in Aggressive Breast Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 15;11(11):1797. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111797. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31731707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blackburn E.H., Epel E.S., Lin J.. Human telomere biology: a contributory and interactive factor in aging, disease risks, and protection. Science. 2015; 350:1193–1198. - PubMed
-
- Blasco M.A. Telomere length, stem cells and aging. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007; 3:640–649. - PubMed
-
- Hänsel-Hertsch R., Di Antonio M., Balasubramanian S.. DNA G-quadruplexes in the human genome: detection, functions and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017; 18:279–284. - PubMed
-
- Neidle S. Quadruplex nucleic acids as targets for anticancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017; 1:0041.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

