RsaC sRNA modulates the oxidative stress response of Staphylococcus aureus during manganese starvation
- PMID: 31504767
- PMCID: PMC6765141
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz728
RsaC sRNA modulates the oxidative stress response of Staphylococcus aureus during manganese starvation
Abstract
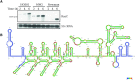
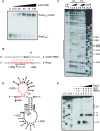
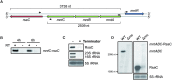
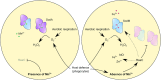
The human opportunistic pathogen Staphylococcus aureus produces numerous small regulatory RNAs (sRNAs) for which functions are still poorly understood. Here, we focused on an atypical and large sRNA called RsaC. Its length varies between different isolates due to the presence of repeated sequences at the 5' end while its 3' part is structurally independent and highly conserved. Using MS2-affinity purification coupled with RNA sequencing (MAPS) and quantitative differential proteomics, sodA mRNA was identified as a primary target of RsaC sRNA. SodA is a Mn-dependent superoxide dismutase involved in oxidative stress response. Remarkably, rsaC gene is co-transcribed with the major manganese ABC transporter MntABC and, consequently, RsaC is mainly produced in response to Mn starvation. This 3'UTR-derived sRNA is released from mntABC-RsaC precursor after cleavage by RNase III. The mature and stable form of RsaC inhibits the synthesis of the Mn-containing enzyme SodA synthesis and favors the oxidative stress response mediated by SodM, an alternative SOD enzyme using either Mn or Fe as co-factor. In addition, other putative targets of RsaC are involved in oxidative stress (ROS and NOS) and metal homeostasis (Fe and Zn). Consequently, RsaC may balance two interconnected defensive responses, i.e. oxidative stress and metal-dependent nutritional immunity.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A manganese-sparing response balances competing cellular demands to enable Staphylococcus aureus infection.mBio. 2025 Sep 10;16(9):e0143925. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01439-25. Epub 2025 Aug 18. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40824060 Free PMC article.
-
The Staphylococcus aureus ABC-Type Manganese Transporter MntABC Is Critical for Reinitiation of Bacterial Replication Following Exposure to Phagocytic Oxidative Burst.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 17;10(9):e0138350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138350. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26379037 Free PMC article.
-
The 3'UTR-derived sRNA RsaG coordinates redox homeostasis and metabolism adaptation in response to glucose-6-phosphate uptake in Staphylococcus aureus.Mol Microbiol. 2022 Jan;117(1):193-214. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14845. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Mol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34783400
-
Emerging functions for the Staphylococcus aureus RNome.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(12):e1003767. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003767. Epub 2013 Dec 12. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24348246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From the genome sequence via the proteome to cell physiology - Pathoproteomics and pathophysiology of Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Med Microbiol. 2018 Aug;308(6):545-557. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Int J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29398252 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of nickel-regulated small RNA in modulation of Helicobacter pylori virulence factors.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Nov 6;10(31):11283-11291. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i31.11283. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36387830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Reveals the Genes Involved in Survival at Low Temperature.Foods. 2022 Mar 29;11(7):996. doi: 10.3390/foods11070996. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35407083 Free PMC article.
-
Forecasting Staphylococcus aureus Infections Using Genome-Wide Association Studies, Machine Learning, and Transcriptomic Approaches.mSystems. 2022 Aug 30;7(4):e0037822. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00378-22. Epub 2022 Jul 5. mSystems. 2022. PMID: 35862809 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and Versatility in Small RNA-Mediated Regulation in Bacterial Pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 10;12:719977. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.719977. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34447363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A key antisense sRNA modulates the oxidative stress response and virulence in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jul 23;17(7):e1009762. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009762. eCollection 2021 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34297775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imlay J.A. Pathways of oxidative damage. Annu. Rev. microbiol. 2003; 57:395–418. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

