Programmed genome rearrangements in Oxytricha produce transcriptionally active extrachromosomal circular DNA
- PMID: 31504770
- PMCID: PMC6765146
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz725
Programmed genome rearrangements in Oxytricha produce transcriptionally active extrachromosomal circular DNA
Abstract
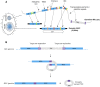
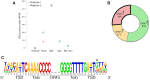
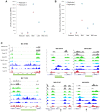
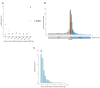
Extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) is both a driver of eukaryotic genome instability and a product of programmed genome rearrangements, but its extent had not been surveyed in Oxytricha, a ciliate with elaborate DNA elimination and translocation during development. Here, we captured rearrangement-specific circular DNA molecules across the genome to gain insight into its processes of programmed genome rearrangement. We recovered thousands of circularly excised Tc1/mariner-type transposable elements and high confidence non-repetitive germline-limited loci. We verified their bona fide circular topology using circular DNA deep-sequencing, 2D gel electrophoresis and inverse polymerase chain reaction. In contrast to the precise circular excision of transposable elements, we report widespread heterogeneity in the circular excision of non-repetitive germline-limited loci. We also demonstrate that circular DNAs are transcribed in Oxytricha, producing rearrangement-specific long non-coding RNAs. The programmed formation of thousands of eccDNA molecules makes Oxytricha a model system for studying nucleic acid topology. It also suggests involvement of eccDNA in programmed genome rearrangement.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Programmed Genome Rearrangements in the Ciliate Oxytricha.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Dec;2(6):10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0025-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0025-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26104449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oxytricha trifallax macronuclear genome: a complex eukaryotic genome with 16,000 tiny chromosomes.PLoS Biol. 2013;11(1):e1001473. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001473. Epub 2013 Jan 29. PLoS Biol. 2013. PMID: 23382650 Free PMC article.
-
A functional role for transposases in a large eukaryotic genome.Science. 2009 May 15;324(5929):935-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1170023. Epub 2009 Apr 16. Science. 2009. PMID: 19372392 Free PMC article.
-
Thousands of RNA-cached copies of whole chromosomes are present in the ciliate Oxytricha during development.RNA. 2017 Aug;23(8):1200-1208. doi: 10.1261/rna.058511.116. Epub 2017 Apr 27. RNA. 2017. PMID: 28450531 Free PMC article.
-
Origin, structure and function of millions of chromosomes present in the macronucleus of unicellular eukaryotic ciliate, Oxytricha trifallax: a model organism for transgenerationally programmed genome rearrangements.J Genet. 2015 Jun;94(2):171-6. doi: 10.1007/s12041-015-0504-2. J Genet. 2015. PMID: 26174664 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Extrachromosomal Circular DNAs: Origin, formation and emerging function in Cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Mar 2;17(4):1010-1025. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.54614. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33867825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extrachromosomal Circular DNA: A New Target in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 14;12:814504. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.814504. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35494014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Characterization of Extrachromosomal Circular DNA in Human Placentas With Fetal Growth Restriction.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 21;12:780779. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.780779. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34992600 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the mysteries of extrachromosomal circular DNA: from generation to clinical relevance in human cancers and health.Mol Cancer. 2024 Dec 20;23(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02187-5. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39707444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Noncoding RNAs in Ciliate Genome Architecture.J Mol Biol. 2020 Jul 10;432(15):4186-4198. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.12.042. Epub 2020 Jan 10. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31926952 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

