Is high-volume post-dilution haemodiafiltration associated with risk of fluid volume imbalance? A national multicentre cross-sectional cohort study
- PMID: 31504813
- PMCID: PMC6887955
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfz141
Is high-volume post-dilution haemodiafiltration associated with risk of fluid volume imbalance? A national multicentre cross-sectional cohort study
Abstract
Background: Fluid overload is frequent among hemodialysis (HD) patients. Dialysis therapy itself may favor sodium imbalance from sodium dialysate prescription. As on-line hemodiafiltration (OL-HDF) requires large amounts of dialysate infusion, this technique can expose to fluid accumulation in case of a positive sodium gradient between dialysate and plasma. To evaluate this risk, we have analyzed and compared the fluid status of patients treated with HD or OL-HDF in French NephroCare centers.
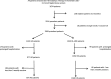
Method: This is a cross-sectional and retrospective analysis of prevalent dialysis patients. Data were extracted from the EUCLID5 data base. Patients were split in 2 groups (HD and OL-HDF) and compared as whole group or matched patients for fluid status criteria including predialysis relative fluid overload (RelFO%) status from the BCM®.
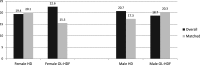
Results: 2242 patients (age 71 years; female: 39%; vintage: 38 months; Charlson index: 6) were studied. 58% of the cohort were prescribed post-dilution OL-HDF. Comparing the HD and OL-HDF groups, there was no difference between HD and OL-HDF patients regarding the predialysis systolic BP, the interdialytic weight gain, the dialysate-plasma sodium gradient, and the predialysis RelFO%. The stepwise logistic regression did not find dialysis modality (HD or OL-HDF) associated with fluid overload or high predialysis systolic blood pressure. In OL-HDF patients, monthly average convective or weekly infusion volumes per session were not related with the presence of fluid overload.
Conclusions: In this cross-sectional study we did not find association between the use of post-dilution OL-HDF and markers of fluid volume excess. Aligned dialysis fluid sodium concentrations to patient predialysis plasma sodium and regular monitoring of fluid volume status by bioimpedance spectroscopy may have been helpful to manage adequately the fluid status in both OL-HDF and HD patients.
Keywords: bioimpedance; fluid overload; post-dilution haemodiafiltration; sodium balance; sodium gradient.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative assessment of sodium mass removal using ionic dialysance and sodium gradient as a proxy tool: Comparison of high-flux hemodialysis versus online hemodiafiltration.Artif Organs. 2021 Aug;45(8):E280-E292. doi: 10.1111/aor.13923. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Artif Organs. 2021. PMID: 33507535
-
Optimal therapeutic conditions for online hemodiafiltration.Contrib Nephrol. 2011;168:28-38. doi: 10.1159/000321742. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 20938123
-
Albumin losses during hemodiafiltration: all dialyzers are not created equal - a case report.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Oct 28;20(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1567-8. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31660886 Free PMC article.
-
Why choose high volume online post-dilution hemodiafiltration?J Nephrol. 2017 Apr;30(2):181-186. doi: 10.1007/s40620-016-0343-0. Epub 2016 Sep 1. J Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27586123 Review.
-
Personalized Management of Sodium and Volume Imbalance in Hemodialysis to Mitigate High Costs of Hospitalization.Blood Purif. 2023;52(6):564-577. doi: 10.1159/000530816. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Blood Purif. 2023. PMID: 37290421 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of intra- and interdialytic sodium balance and restriction in dialysis therapies.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 4;10:1268319. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1268319. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38111694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Donnan equilibrium is still valid in high-volume HDF.Int J Artif Organs. 2024 Dec;47(12):867-875. doi: 10.1177/03913988241296699. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Int J Artif Organs. 2024. PMID: 39538421 Free PMC article.
-
Why should we focus on high-volume hemodiafiltration?Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2022 Nov;41(6):670-681. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.21.268. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 35286790 Free PMC article.
-
Why High-Volume Post-Dilution Hemodiafiltration Should Be the New Standard in Dialysis Care: A Comprehensive Review of Clinical Outcomes and Mechanisms.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 9;14(14):4860. doi: 10.3390/jcm14144860. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40725552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Clinical Benefits of High-Volume Hemodiafiltration: Optimizing the Removal of Medium-Weight Uremic Toxins and Beyond.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;15(9):531. doi: 10.3390/toxins15090531. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755957 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nordio M, Tessitore N, Feriani M. et al. Mortality in the Veneto population on renal replacement therapy. J Nephrol 2013; 26 (Suppl 20): S23–S33 - PubMed
-
- Kayikcioglu M, Tumuklu M, Ozkahya M. et al. The benefit of salt restriction in the treatment of end-stage renal disease by haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2008; 24: 956–962 - PubMed
-
- Davenport A, Cox C, Thuraisingham R.. Achieving blood pressure targets during dialysis improves control but increases intradialytic hypotension. Kidney Int 2008; 73: 759–764 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

