Mechanisms of Dupilumab
- PMID: 31505066
- PMCID: PMC6930967
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.13491
Mechanisms of Dupilumab
Abstract
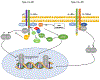
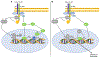
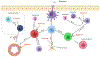
The Th2 cytokines interleukin 4 (IL-4) and IL-13 and the heterodimeric IL-4 receptor (IL-4R) complexes that they interact with play a key role in the pathogenesis of allergic disorders. Dupilumab is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody that targets the IL-4 receptor alpha chain (IL-4Rα), common to both IL-4R complexes: type 1 (IL-4Rα/γc; IL-4 specific) and type 2 (IL-4Rα/IL-13Rα1; IL-4 and IL-13 specific). In this review, we detail the current state of knowledge of the different signalling pathways coupled to the IL-4R complexes and examine the possible mechanisms of Dupilumab action and survey its clinical efficacy in different allergic disorders. The development of Dupilumab and the widening spectrum of its clinical applications is relevant to the current emphasis on precision medicine approaches to the blockade of pathways involved in allergic diseases.
Keywords: IL-4R; T cells; T-reg; asthma; atopic dermatitis; dupilumab; food allergy.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
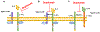
References
-
- Skolnik NS, Carnahan SP. Primary care of asthma: new options for severe eosinophilic asthma. Curr Med Res Opin. 2019:1. - PubMed
-
- Shamoun L, Skarstedt M, Andersson RE, Wagsater D, Dimberg J. Association study on IL-4, IL-4Ralpha and IL-13 genetic polymorphisms in Swedish patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;487:101–106. - PubMed
-
- Chatila TA. Interleukin-4 receptor signaling pathways in asthma pathogenesis. Trends Mol Med. 2004;10(10):493–499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

