FMK, an Inhibitor of p90RSK, Inhibits High Glucose-Induced TXNIP Expression via Regulation of ChREBP in Pancreatic β Cells
- PMID: 31505737
- PMCID: PMC6770409
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20184424
FMK, an Inhibitor of p90RSK, Inhibits High Glucose-Induced TXNIP Expression via Regulation of ChREBP in Pancreatic β Cells
Abstract
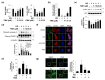
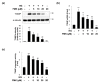
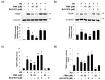
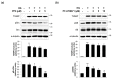
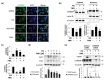
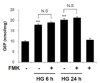
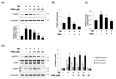
Hyperglycemia is the major characteristic of diabetes mellitus, and a chronically high glucose (HG) level causes β-cell glucolipotoxicity, which is characterized by lipid accumulation, impaired β-cell function, and apoptosis. TXNIP (Thioredoxin-interacting protein) is a key mediator of diabetic β-cell apoptosis and dysfunction in diabetes, and thus, its regulation represents a therapeutic target. Recent studies have reported that p90RSK is implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy and nephropathy. In this study, we used FMK (a p90RSK inhibitor) to determine whether inhibition of p90RSK protects β-cells from chronic HG-induced TXNIP expression and to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying the effect of FMK on its expression. In INS-1 pancreatic β-cells, HG-induced β-cell dysfunction, apoptosis, and ROS generation were significantly diminished by FMK. In contrast BI-D1870 (another p90RSK inhibitor) did not attenuate HG-induced TXNIP promoter activity or TXNIP expression. In addition, HG-induced nuclear translocation of ChREBP and its transcriptional target molecules were found to be regulated by FMK. These results demonstrate that HG-induced pancreatic β-cell dysfunction resulting in HG conditions is associated with TXNIP expression, and that FMK is responsible for HG-stimulated TXNIP gene expression by inactivating the regulation of ChREBP in pancreatic β-cells. Taken together, these findings suggest FMK may protect against HG-induced β-cell dysfunction and TXNIP expression by ChREBP regulation in pancreatic β-cells, and that FMK is a potential therapeutic reagent for the drug development of diabetes and its complications.
Keywords: ChREBP; FMK; INS-1; TXNIP; p90RSK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FOXO1 competes with carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) and inhibits thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) transcription in pancreatic beta cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 9;288(32):23194-202. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.473082. Epub 2013 Jun 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23803610 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) mediates nutrient regulation of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) in pancreatic beta-cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28804. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028804. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22194917 Free PMC article.
-
ChREBP deficiency alleviates apoptosis by inhibiting TXNIP/oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy.J Diabetes Complications. 2021 Dec;35(12):108050. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2021.108050. Epub 2021 Sep 23. J Diabetes Complications. 2021. PMID: 34600826
-
Diabetes pathogenic mechanisms and potential new therapies based upon a novel target called TXNIP.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018 Apr;25(2):75-80. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000391. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018. PMID: 29356688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minireview: Thioredoxin-interacting protein: regulation and function in the pancreatic β-cell.Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Aug;28(8):1211-20. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1095. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Mol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24911120 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thioredoxin-interacting protein in diabetic retinal neurodegeneration: A novel potential therapeutic target for diabetic retinopathy.Front Neurosci. 2022 Aug 9;16:957667. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.957667. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36017183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hexokinase-linked glycolytic overload and unscheduled glycolysis in hyperglycemia-induced pathogenesis of insulin resistance, beta-cell glucotoxicity, and diabetic vascular complications.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 16;14:1268308. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1268308. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38292764 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of insulin secretion induced by low 4-cresol dose involves the RPS6KA3 signalling pathway.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 24;19(10):e0310370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310370. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39446839 Free PMC article.
-
A novel ribosomal protein S6 kinase 2 inhibitor attenuates the malignant phenotype of cutaneous malignant melanoma cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13555-13570. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2080364. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 36700473 Free PMC article.
-
The Novel Role of Metabolism-Associated Molecular Patterns in Sepsis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jun 2;12:915099. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.915099. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35719361 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

