Bioactive Aliphatic Sulfates from Marine Invertebrates
- PMID: 31505775
- PMCID: PMC6780655
- DOI: 10.3390/md17090527
Bioactive Aliphatic Sulfates from Marine Invertebrates
Abstract
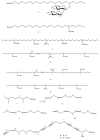
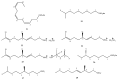
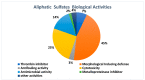
The occurrence of sulfated steroids and phenolics in marine organisms is quite widespread, being typically reported from Echinoderms. In contrast, alkane and alkene aliphatic sulfates are considerably rarer with examples being reported from a diverse array of organisms including echinoderms, sponges and ascidians. While no ecological roles for these metabolites have been proposed, they do exhibit a diverse array of biological activities including thrombin inhibition; the ability to induce metamorphosis in larvae; antiproliferative, antibacterial and antifungal properties; and metalloproteinase inhibition. Of particular interest and an avenue for future development is the finding of antifouling properties with low or nontoxic effects to the environment. This review focuses on alkyl sulfates and related sulfamates, their structures and biological activities. Spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques that can be used to recognize the presence of sulfate groups are also discussed, data for which will enhance the ability of researchers to recognize this class of chemically- and biologically-interesting marine natural products.
Keywords: NMR data; aliphatic sulfate; alkane sulfate; alkene sulfate; alkyl sulfate; bioactivity; marine invertebrates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Marine natural products.Nat Prod Rep. 2021 Mar 4;38(2):362-413. doi: 10.1039/d0np00089b. Nat Prod Rep. 2021. PMID: 33570537 Review.
-
Biomaterials and Bioactive Natural Products from Marine Invertebrates: From Basic Research to Innovative Applications.Mar Drugs. 2022 Mar 22;20(4):219. doi: 10.3390/md20040219. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35447892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycosaminoglycans analogs from marine invertebrates: structure, biological effects, and potential as new therapeutics.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Sep 10;4:123. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00123. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25309878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine natural products.Nat Prod Rep. 2018 Jan 16;35(1):8-53. doi: 10.1039/c7np00052a. Nat Prod Rep. 2018. PMID: 29335692 Review.
-
Bioprospecting of marine invertebrates for new natural products - a chemical and zoogeographical perspective.Molecules. 2012 Aug 16;17(8):9842-54. doi: 10.3390/molecules17089842. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22898739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zygo-Albuside A: New Saponin from Zygophyllum album L. with Significant Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Antiapoptotic Effects against Methotrexate-Induced Testicular Damage.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 16;23(18):10799. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810799. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142712 Free PMC article.
-
Gracilosulfates A-G, Monosulfated Polyoxygenated Steroids from the Marine Sponge Haliclona gracilis.Mar Drugs. 2020 Aug 30;18(9):454. doi: 10.3390/md18090454. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32872590 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive metabolomics of Philippine Stichopus cf. horrens reveals diverse classes of valuable small molecules for biomedical applications.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 6;18(12):e0294535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294535. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38055702 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive molecules from ciliates: Structure, activity, and applicative potential.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2022 Sep;69(5):e12887. doi: 10.1111/jeu.12887. Epub 2022 Jan 28. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35014102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfated and Sulfur-Containing Steroids and Their Pharmacological Profile.Mar Drugs. 2021 Apr 24;19(5):240. doi: 10.3390/md19050240. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33923288 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hu X., Liu J., Liu H., Zhuang G., Xun L. Sulfur metabolism by marine heterotrophic bacteria involved in sulfur cycling in the ocean. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018;61:1369–1378. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9234-x. - DOI
-
- Roccatagliata A.J., Mater M.S., Seldes A.M., Zea S., Duque C. A new sulfated alkene from the ophiuroid Ophiocoma echinata. J. Nat. Prod. 1997;60:285–286. doi: 10.1021/np9606198. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

