Development and Characterization of the Solvent-Assisted Active Loading Technology (SALT) for Liposomal Loading of Poorly Water-Soluble Compounds
- PMID: 31505795
- PMCID: PMC6781273
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11090465
Development and Characterization of the Solvent-Assisted Active Loading Technology (SALT) for Liposomal Loading of Poorly Water-Soluble Compounds
Abstract
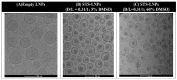
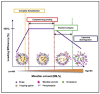
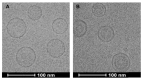
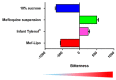
A large proportion of pharmaceutical compounds exhibit poor water solubility, impacting their delivery. These compounds can be passively encapsulated in the lipid bilayer of liposomes to improve their water solubility, but the loading capacity and stability are poor, leading to burst drug leakage. The solvent-assisted active loading technology (SALT) was developed to promote active loading of poorly soluble drugs in the liposomal core to improve the encapsulation efficiency and formulation stability. By adding a small volume (~5 vol%) of a water miscible solvent to the liposomal loading mixture, we achieved complete, rapid loading of a range of poorly soluble compounds and attained a high drug-to-lipid ratio with stable drug retention. This led to improvements in the circulation half-life, tolerability, and efficacy profiles. In this mini-review, we summarize our results from three studies demonstrating that SALT is a robust and versatile platform to improve active loading of poorly water-soluble compounds. We have validated SALT as a tool for improving drug solubility, liposomal loading efficiency and retention, stability, palatability, and pharmacokinetics (PK), while retaining the ability of the compounds to exert pharmacological effects.
Keywords: cancer; child friendly formulation; gambogic acid; liposome; loading gradients; mefloquine; remote loading; staurosporine; water miscible solvents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A solvent-assisted active loading technology to prepare gambogic acid and all-trans retinoic acid co-encapsulated liposomes for synergistic anticancer therapy.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020 Feb;10(1):146-158. doi: 10.1007/s13346-019-00669-4. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 31529371
-
Systemic study of solvent-assisted active loading of gambogic acid into liposomes and its formulation optimization for improved delivery.Biomaterials. 2018 Jun;166:13-26. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 3. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 29529479
-
Development of a Rapidly Dissolvable Oral Pediatric Formulation for Mefloquine Using Liposomes.Mol Pharm. 2017 Jun 5;14(6):1969-1979. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00077. Epub 2017 May 9. Mol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28460165
-
Approaches to Address PK-PD Challenges of Conventional Liposome Formulation with Special Reference to Cancer, Alzheimer's, Diabetes, and Glaucoma: An Update on Modified Liposomal Drug Delivery System.Curr Drug Metab. 2022;23(9):678-692. doi: 10.2174/1389200223666220609141459. Curr Drug Metab. 2022. PMID: 35692131 Review.
-
Factors affecting microencapsulation of drugs in liposomes.J Microencapsul. 1995 May-Jun;12(3):229-46. doi: 10.3109/02652049509010292. J Microencapsul. 1995. PMID: 7650588 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Effect of Saccharides on Freeze-Dried Liposomes Encapsulating Drugs.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Dec 17;7:424. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00424. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31921827 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the loading and release kinetics of the vincristine sulfate liposomes and its anti-breast cancer activity.Int J Pharm X. 2024 May 31;7:100258. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2024.100258. eCollection 2024 Jun. Int J Pharm X. 2024. PMID: 38912324 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile Encapsulation and Synthesis of Potent Liposomes by Thermal Equilibration.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Mar 11;12(3):319. doi: 10.3390/membranes12030319. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35323794 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Targeting and Stimuli-Triggered Liposomal Drug Delivery in Cancer Treatment.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021 Jun 1;4(3):1028-1049. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00066. eCollection 2021 Jun 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 34151199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liposomes: An Emerging Strategy for the Effective Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2025;21(2):123-143. doi: 10.2174/0115733971284274240215064826. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2025. PMID: 38441022 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

