Identification and Characterization of a Novel Protein ASP-3 Purified from Arca subcrenata and Its Antitumor Mechanism
- PMID: 31505835
- PMCID: PMC6780846
- DOI: 10.3390/md17090528
Identification and Characterization of a Novel Protein ASP-3 Purified from Arca subcrenata and Its Antitumor Mechanism
Abstract
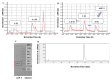
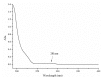
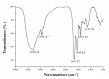
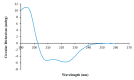
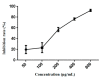
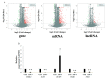
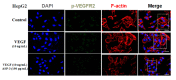
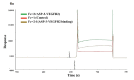
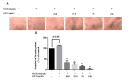
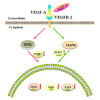
Diverse bioactive substances derived from marine organisms have been attracting growing attention. Besides small molecules and polypeptides, numerous studies have shown that marine proteins also exhibit antitumor activities. Small anticancer proteins can be expressed in vivo by viral vectors to exert local and long-term anticancer effects. Herein, we purified and characterized a novel protein (ASP-3) with unique antitumor activity from Arca subcrenata Lischke. The ASP-3 contains 179 amino acids with a molecular weight of 20.6 kDa. The spectral characterization of ASP-3 was elucidated using Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and Circular Dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Being identified as a sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein, ASP-3 exhibited strong inhibitory effects on the proliferation of Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells with an IC50 value of 171.18 ± 18.59 μg/mL, measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The RNA-seq analysis showed that ASP-3 regulated the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) signaling pathway in HepG2 cells. Immunofluorescence results indicated that ASP-3 effectively reduced VEGFR2 phosphorylation in HepG2 cells and affected the downstream components of VEGF signaling pathways. The surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis further demonstrated that ASP-3 direct interacted with VEGFR2. More importantly, the therapeutic potential of ASP-3 as an anti-angiogenesis agent was further confirmed by an in vitro model using VEGF-induced tube formation assay of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), as well as an in vivo model using transgenic zebrafish model. Taken together, the ASP-3 provides a good framework for the development of even more potent anticancer proteins and provides important weapon for cancer treatment using novel approaches such as gene therapy.
Keywords: Arca subcrenata protein; antitumor mechanism; structural characterization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dual effects of targeting neuropilin-1 in lenvatinib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma: inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024 Oct 1;327(4):C1150-C1161. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00511.2024. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39250819
-
Antiangiogenic mechanisms of PJ-8, a novel inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling.Carcinogenesis. 2012 May;33(5):1022-30. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs127. Epub 2012 Mar 20. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22436611
-
Evodiamine exerts anti-tumor effects against hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibiting β-catenin-mediated angiogenesis.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):12791-12803. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5251-3. Epub 2016 Jul 23. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27449032
-
The epigallocatechin gallate derivative Y6 inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting angiogenesis in MAPK/ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT/ HIF-1α/VEGF dependent pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Sep 15;259:112852. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112852. Epub 2020 Apr 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32278759
-
SKLB610: a novel potential inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in vivo.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;27(5):565-74. doi: 10.1159/000329978. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21691074
Cited by
-
Investigation of Anticancer Peptides Derived from Arca Species Using In Silico Analysis.Molecules. 2025 Apr 7;30(7):1640. doi: 10.3390/molecules30071640. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40286246 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances of the Zebrafish Model in the Discovery of Marine Bioactive Molecules.Mar Drugs. 2024 Nov 30;22(12):540. doi: 10.3390/md22120540. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39728115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNA-related antitumor mechanisms of marine-derived agents.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 1;13:1053556. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1053556. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36532760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developing natural marine products for treating liver diseases.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Mar 16;10(8):2369-2381. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i8.2369. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 35434070 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Helena C., Alsinet C., Villanueva A. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011;35:821–825. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

