Patient Satisfaction with Health Care Services; An Application of Physician's Behavior as a Moderator
- PMID: 31505840
- PMCID: PMC6765938
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16183318
Patient Satisfaction with Health Care Services; An Application of Physician's Behavior as a Moderator
Abstract
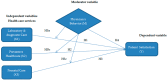
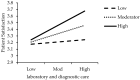
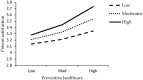
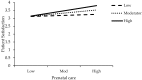
Patient satisfaction is a measure of the extent to which a patient is content with the health care they received from their health care provider. Patient satisfaction is one of the most important factors to determine the success of a health care facility. The purpose of this study was to determine patient satisfaction with healthcare services and encompass the physician's behavior as moderation between patient satisfaction and healthcare services. The study seeks to measure the health care services, like a laboratory and diagnostic care, preventive healthcare and prenatal care, to patient satisfaction in the public health sectors of Pakistan. A descriptive survey research design was used for this study. The target population was patients from the out-patient department (OPD) of three public hospitals from Pakistan. By using the convenient sampling technique, 290 sample participants were selected from the target population. The reliability scales were tallied by using Cronbach's Alpha. The findings of the study are gleaned by using regression to explore patient satisfaction with the health care services, and whether or not the physician's behavior moderates the link of patient satisfaction and healthcare services. SPSS Hayes process was used for the moderation effect of the physician's behavior. The main results of the regression analysis validate that health care services, such as laboratory and diagnostic care, preventive healthcare, and prenatal care, have a significant and positive effect on patient satisfaction. Specifically, the study suggests that the physician's behavior significantly moderates the effect of health care services on the satisfaction of patients. The overall opinions about the satisfaction level of patients for the availability of health services in the hospitals were good. The degree of satisfaction was satisfactory with respect to laboratory and diagnostic care, preventive healthcare, and prenatal care services. Based on the outcomes, the study confirms that the proposed hypotheses are statistically significant. Furthermore, the directions for future research of the study are offered.
Keywords: Pakistan; healthcare services; laboratory and diagnostic care; patient satisfaction; physician’s behavior; prenatal care; preventive healthcare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promoting OPD Patient Satisfaction through Different Healthcare Determinants: A Study of Public Sector Hospitals.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Oct 2;16(19):3719. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16193719. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31581643 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring OPD Patient Satisfaction with Different Service Delivery Aspects at Public Hospitals in Pakistan.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jul 2;16(13):2340. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16132340. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31269722 Free PMC article.
-
Does the physician's emotional intelligence matter? Impacts of the physician's emotional intelligence on the trust, patient-physician relationship, and satisfaction.Health Care Manage Rev. 2008 Oct-Dec;33(4):280-8. doi: 10.1097/01.HCM.0000318765.52148.b3. Health Care Manage Rev. 2008. PMID: 18815493
-
Patients' reaction to the ethical conduct of radiographers and staff services as predictors of radiological experience satisfaction: a cross-sectional study.BMC Med Ethics. 2015 Oct 8;16(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12910-015-0062-4. BMC Med Ethics. 2015. PMID: 26450173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Physician's Visiting List, Diary, and Book of Engagements, for 1861.N Am Medchir Rev. 1861 Jan;5(1):64-65. N Am Medchir Rev. 1861. PMID: 38080140 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Prioritizing and Overcoming Barriers to e-Health Use among Elderly People: Implementation of the Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP).J Healthc Eng. 2022 Apr 11;2022:7852806. doi: 10.1155/2022/7852806. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35449830 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive Retraining and Functional Treatment (CRAFT) for adults with cancer related cognitive impairment: a preliminary efficacy study.Support Care Cancer. 2023 Feb 7;31(3):152. doi: 10.1007/s00520-023-07611-y. Support Care Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36746805 Free PMC article.
-
Human Resource Management as an Area of Changes in a Healthcare Institution.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2023 Jan 6;16:31-41. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S388185. eCollection 2023. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2023. PMID: 36636035 Free PMC article.
-
The Contribution of Sustainable Tourism toEconomic Growth and Employment in Pakistan.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Oct 8;16(19):3785. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16193785. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31597376 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Coronavirus-19 on Mental Condition of International Students in China.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Jan 3;12:738828. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.738828. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35046847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li M., Lowrie D.B., Huang C.-Y., Lu X.-C., Zhu Y.-C., Wu X.-H., Shayiti M., Tan Q.-Z., Yang H.-L., Chen S.-Y. Evaluating patients’ perception of service quality at hospitals in nine Chinese cities by use of the ServQual scale. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015;5:497–504. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.02.003. - DOI
-
- Bleustein C., Rothschild D.B., Valen A., Valatis E., Schweitzer L., Jones R. Wait times, patient satisfaction scores, and the perception of care. Am. J. Manag. Care. 2014;20:393–400. - PubMed
-
- Karatepe O.M., Yavas U., Babakus E. Measuring service quality of banks: Scale development and validation. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2005;12:373–383. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2005.01.001. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

