Correction: Tugault-Lafleur C.N. and Black J.L. "Differences in the Quantity and Types of Foods and Beverages Consumed by Canadians between 2004 and 2015" Nutrients 2019, 11, 526
- PMID: 31505842
- PMCID: PMC6769503
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11092160
Correction: Tugault-Lafleur C.N. and Black J.L. "Differences in the Quantity and Types of Foods and Beverages Consumed by Canadians between 2004 and 2015" Nutrients 2019, 11, 526
Abstract
We would like to submit the following corrections to our recently published paper [...].
Figures
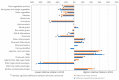
Erratum for
-
Differences in the Quantity and Types of Foods and Beverages Consumed by Canadians between 2004 and 2015.Nutrients. 2019 Feb 28;11(3):526. doi: 10.3390/nu11030526. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30823448 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Beverage intake among preschool children and its effect on weight status.Pediatrics. 2006 Oct;118(4):e1010-8. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-2348. Pediatrics. 2006. PMID: 17015497
-
Correction: Jang, S.-E.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 and Lactobacillus acidophilus La-14 Attenuate Gardnerella vaginalis-Infected Bacterial Vaginosis in Mice. Nutrients 2017, 9, 531.Nutrients. 2017 Jul 7;9(7):715. doi: 10.3390/nu9070715. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28686189 Free PMC article.
-
Correction: Grieger, J.A.; et al.: Comparing the Nutritional Impact of Dietary Strategies to Reduce Discretionary Choice Intake in the Australian Adult Population: A Simulation Modelling Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 442.Nutrients. 2017 Aug 9;9(8):851. doi: 10.3390/nu9080851. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28792462 Free PMC article.
-
An introduction to the traditional fermented foods and beverages of Turkey.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2011 Mar;51(3):248-60. doi: 10.1080/10408390903569640. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21390945 Review.
-
Traditional low-alcoholic and non-alcoholic fermented beverages consumed in European countries: a neglected food group.Nutr Res Rev. 2017 Jun;30(1):1-24. doi: 10.1017/S0954422416000202. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Nutr Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28115036 Review.
References
-
- Institute of Medicine . Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein and Amino Acids. National Academy Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

