Effect of Diabetes Education Through Pattern Management on Self-Care and Self-Efficacy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 31505892
- PMCID: PMC6765832
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16183323
Effect of Diabetes Education Through Pattern Management on Self-Care and Self-Efficacy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
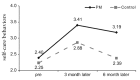
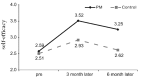
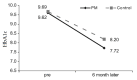
This study investigated the effect of applying a customized diabetes education program through pattern management (PM), using continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) results, on individual self-care behaviors and self-efficacy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Patients with type 2 diabetes who had never received diabetes education, enrolled from March to September 2017, were sequentially assigned to either PM education or control groups. In the PM education group, the CGMS test was first conducted one week before diabetes education and repeated three times by PM in order to obtain data on self-care behaviors and self-efficacy. These results were then compared before and after education at three and six months. The control group received the traditional diabetes education. Self-efficacy showed statistically significant interactions between the two groups over time, indicating a significant difference in the degree of self-efficacy between the PM education and control groups. Diabetes education by PM using CGMS result analysis improved life habits with a positive influence on self-care behaviors and self-efficacy for diabetes management. Further studies are needed to further develop and apply individual diabetes education programs in order to sustain the effects of self-care behaviors and self-efficacy in patients with diabetes who experience a decrease in self-efficacy after three months of education.
Keywords: Diabetes education; self-care; self-efficacy; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Report on Diabetes. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- Statistics Korea Yearly statistics of causes of death. [(accessed on 22 September 2017)]; Available online: http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/2/6/2/index.board?bmode=read&bSe...
-
- Choi K.A., Jang S.M., Nam H.W. Self-management practices, and disturbance of elderly diabetics. Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32:280–289. doi: 10.4093/kdj.2008.32.3.280. - DOI
-
- Kuznetsov L., Griffin S.J., Davies M.J., Lauritzen T., Khunti K., Rutten G.E., Simmons R.K. Diabetes-specific quality of life but not health status is independently associated with glycaemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional analysis of the ADDITION-Europe trial cohort. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014;104:281–287. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2013.12.029. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Korean Diabetes Association . 2015 Practice Guideline on Diabetes. Korean Diabetes Association; Seoul, Korea: 2015.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

