Optimization of Production Parameters for Probiotic Lactobacillus Strains as Feed Additive
- PMID: 31505895
- PMCID: PMC6767249
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24183286
Optimization of Production Parameters for Probiotic Lactobacillus Strains as Feed Additive
Abstract
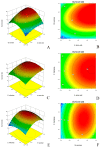
In animal nutrition, probiotics are considered as desirable alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters. The beneficial effects of probiotics primarily depend on their viability in feed, which demands technical optimization of biomass production, since processing and storage capacities are often strain-specific. In this study, we optimized the production parameters for two broiler-derived probiotic lactobacilli (L. salivarius and L. agilis). Carbohydrate utilization of both strains was determined and preferred substrates that boosted biomass production in lab-scale fermentations were selected. The strains showed good aerobic tolerance, which resulted in easier scale-up production. For the freeze-drying process, the response surface methodology was applied to optimize the composition of cryoprotective media. A quadratic polynomial model was built to study three protective factors (skim milk, sucrose, and trehalose) and to predict the optimal working conditions for maximum viability. The optimal combination of protectants was 0.14g/mL skim milk/ 0.08 g/mL sucrose/ 0.09 g/mL trehalose (L. salivarius) and 0.15g/mL skim milk/ 0.08 g/mL sucrose/ 0.07 g/mL (L. agilis), respectively. Furthermore, the in-feed stabilities of the probiotic strains were evaluated under different conditions. Our results indicate that the chosen protectants exerted an extensive protection on strains during the storage. Although only storage of the strains at 4 °C retained the maximum stability of both Lactobacillus strains, the employed protectant matrix showed promising results at room temperature.
Keywords: freeze-drying; in-feed stability; optimization procedure; probiotic; response surface method.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Determination of Optimized Growth Medium and Cryoprotective Additives to Enhance the Growth and Survival of Lactobacillus salivarius.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 May 28;28(5):718-731. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1801.01059. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29551016
-
Survival and stability of Lactobacillus fermentum and Wickerhamomyces anomalus strains upon lyophilisation with different cryoprotectant agents.Food Res Int. 2019 Jan;115:90-94. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.07.044. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Food Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30599986
-
Impact of different cryoprotectants on the survival of freeze-dried Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus casei/paracasei during long-term storage.Benef Microbes. 2015;6(3):381-6. doi: 10.3920/BM2014.0038. Benef Microbes. 2015. PMID: 25380798
-
Improving the drying of Propionibacterium freudenreichii starter cultures.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 May;105(9):3485-3494. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11273-3. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33885925 Review.
-
Advances in polysaccharides for probiotic delivery: Properties, methods, and applications.Carbohydr Polym. 2024 Jan 1;323:121414. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121414. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Carbohydr Polym. 2024. PMID: 37940247 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Direct-Fed Microbials and Phytogenic Feed Additives on Prevalence and Transfer of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase Genes in Broiler Chicken.Microorganisms. 2020 Feb 26;8(3):322. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8030322. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32110912 Free PMC article.
-
Enterococcus faecalis Is a Better Competitor Than Other Lactic Acid Bacteria in the Initial Colonization of Colon of Healthy Newborn Babies at First Week of Their Life.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 29;11:2017. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.02017. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33133027 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Optimization of Lactobacillus acidophilus for Production of Antimicrobial Peptide Acidocin 4356: Scale up from Flask to Lab-Scale Fermenter.Iran J Biotechnol. 2021 Jul 1;19(3):e2686. doi: 10.30498/ijb.2021.218725.2686. eCollection 2021 Jul. Iran J Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34825011 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of the Effects of Different Temperatures and Compositions of Filmogenic Solution on Lactobacillus Salivarius Using Predictive Mathematical Models.Foods. 2020 Dec 23;10(1):25. doi: 10.3390/foods10010025. Foods. 2020. PMID: 33374864 Free PMC article.
-
The Endophytic Pseudomonas sp. S57 for Plant-Growth Promotion and the Biocontrol of Phytopathogenic Fungi and Nematodes.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jul 27;10(8):1531. doi: 10.3390/plants10081531. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grashorn M.A. Use of phytobiotics in broiler nutrition – an alternative to infeed antibiotics? J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2010;19:338–347. doi: 10.22358/jafs/66297/2010. - DOI
-
- Wang H., Ni X., Qing X., Zeng D., Luo M., Liu L., Li G., Pan K., Jing B. Live Probiotic Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 Promotes Growth Performance and Lowers Fat Deposition by Improving Lipid Metabolism, Intestinal Development, and Gut Microflora in Broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2017;8 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01073. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

