miR-206 Promotes Cancer Progression by Targeting Full-Length Neurokinin-1 Receptor in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 31506061
- PMCID: PMC6740052
- DOI: 10.1177/1533033819875168
miR-206 Promotes Cancer Progression by Targeting Full-Length Neurokinin-1 Receptor in Breast Cancer
Abstract
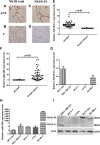
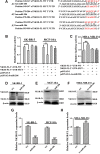
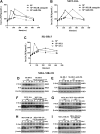
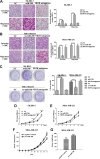
Substance P plays a pivotal role in human cancer development and progression by binding to its receptor, neurokinin-1. Neurokinin-1 has 2 isoforms: full-length neurokinin-1 and truncated neurokinin-1, the latter lacking the cytoplasmic terminal 96-amino acid residues of the full-length protein. We have identified 3 candidate miR-206 target sites within the 3'-untranslated region of the full-length neurokinin-1 gene from bioinformatics database searches. In the present study, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction was performed to quantify the expression of miR-206, and the expression of neurokinin-1 and full-length neurokinin-1 was detected by immunohistochemistry in 82 clinical cases of breast cancer and paired adjacent normal tissues. The miR-206 target gene was demonstrated by using a dual-luciferase reporter assay, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, and Western blotting. Transwell migration and invasion, colony formation, and proliferation assays were performed to evaluate the effects of miR-206 expression on various aspects of breast cancer cell behavior in vitro. We showed that miR-206 expression is upregulated in breast cancer cell lines and breast cancer tissues when compared to that in adjacent normal tissues, and full-length neurokinin-1 expression inversely correlates with Tumor Lymph Node Metastasis (TNM) stage and lymph node metastasis. Western blotting, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, and dual-luciferase reporter assays demonstrated that miR-206 binds the 3'-untranslated region of full-length neurokinin-1 messenger RNA, regulating protein expression. We showed that the overexpression of miR-206 promotes breast cancer cell invasion, migration, proliferation, and colony formation in vitro. The present study furthers the current understanding of the mechanisms underlying breast cancer pathogenesis and may be useful for the development of novel targeted therapies.
Keywords: breast cancer; invasion; microrna-206; neurokinin-1 receptor; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-409-3p regulates cell invasion and metastasis by targeting ZEB1 in breast cancer.IUBMB Life. 2016 May;68(5):394-402. doi: 10.1002/iub.1494. Epub 2016 Apr 15. IUBMB Life. 2016. PMID: 27079864
-
Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-224 promotes the cell growth, migration and invasion by directly targeting RASSF8 in gastric cancer.Mol Cancer. 2017 Feb 7;16(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0603-1. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28173803 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-142-5p Acts as a Significant Regulator Through Promoting Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration in Breast Cancer Modulated by Targeting SORBS1.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan-Dec;18:1533033819892264. doi: 10.1177/1533033819892264. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 31789129 Free PMC article.
-
New insight into the role of substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor system in breast cancer progression and its crosstalk with microRNAs.Clin Genet. 2020 Oct;98(4):322-330. doi: 10.1111/cge.13750. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Clin Genet. 2020. PMID: 32266968 Review.
-
Distant metastasis in breast cancer: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Cancer Biol Ther. 2003 Jan-Feb;2(1):14-21. doi: 10.4161/cbt.188. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12673112 Review.
Cited by
-
ER Negative Breast Cancer and miRNA: There Is More to Decipher Than What the Pathologist Can See!Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 18;11(8):2300. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082300. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-206 as a prognostic and sensitivity biomarker for platinum chemotherapy in epithelial ovarian cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Nov 3;20(1):534. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01623-y. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 33292230 Free PMC article.
-
The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist Aprepitant: An Intelligent Bullet against Cancer?Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 20;12(9):2682. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092682. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32962202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of Differentially Regulated miRNAs in Breast Cancer Progression: Potential Markers for Early Detection and Candidates for Therapy.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 20;12(3):691. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030691. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory role of miRNAs in thyroid and breast cancer progression and insights into their therapeutic manipulation.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022 Oct 3;3:100131. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100131. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 36568259 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, Jemal A. Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):52–62. - PubMed
-
- Matamala N, Vargas MT, Gonzalez-Campora R, et al. Tumor microRNA expression profiling identifies circulating microRNAs for early breast cancer detection. Clin Chem. 2015;61(8):1098–1106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

